Lectin and Lecithin may not be well known in our society, yet these essential nutrients play a pivotal role in maintaining body functioning. Understanding their significance can empower us to make informed dietary choices that support overall well-being.
What is Lectin?
Lectins are an abundant class of glycoproteins found throughout nature, particularly in plants. Lectins play an integral part in various processes within plants as well as providing defenses against pathogens and predators. Lectins can bind to specific carbohydrate molecules on the surface of cells and tissues, and this unique binding property contributes to their various functions.
Plant life contains various lectins which can be found in its leaves, seeds, stems, and roots. Plant guardians serve to prevent animals, insects, or microorganisms from eating their host plant. When consumed by potential predators, lectins may interfere with the digestive process, cause agglutination (clumping) of cells, and even lead to cell damage, making the consumed parts less appealing or toxic.
Lectins can survive digestion enzymes without degrading, providing them with the chance to interact with intestinal tract linings as part of a positive experience. This interaction has led to growing interest and concern about the potential health effects of lectin consumption in human diets.
Although some lectins may be linked with adverse health impacts in certain circumstances, it’s essential to keep in mind that none of them pose any immediate threats to human safety. Certain lectins have demonstrated many health advantages, including fighting cancer and having immune-modulating properties.
It’s crucial to understand that lectin sensitivity or intolerance varies among individuals. Individuals may experience digestive or other illnesses after ingesting food containing certain kinds of lectins; other people remain completely unaffected. Cooking, soaking, fermenting, or sprouting certain foods can help reduce lectin content and may make them more tolerable for some individuals.
Dietary sources of lectins include legumes (lens, beans, and peanuts) as well as grains such as wheat barley, wheat, and rice; tomatoed eggplant pepper plants as well as some seeds and nuts are other common sources. People with specific health conditions or sensitivities may benefit from being mindful of their lectin intake or exploring diets that minimize lectin consumption.
Lectins are a fascinating and complex class of proteins with diverse functions in plants and potential implications for human health. More research must be completed to understand the full effect of Lentins on human physiology and health, so individuals are advised to speak to health experts or registered dietitians to receive personalized dietary advice.
What is Lecithin?
Lecithin, an all-natural fat found in living organisms such as animals and plants, can be found as part of their natural composition. Hydrophobically treated surfaces contain both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) areas to increase surface area coverage by water repulsion or attraction. This unique structure makes lecithin an excellent emulsifier, capable of binding water and oil together, thereby stabilizing emulsions and preventing their separation.
Chemically speaking, lecithin contains multiple constituents including phosphoric acid, choline Glycerol Glycerol, and fatty acids. Choline, one of the key components of lecithin stands out as being an extremely vital nutrient acting as a precursor for Acetylcholine neurotransmitter production. Acetylcholine plays an essential part in nerve signaling and plays many functions connected with muscle control, memory recall, and many cognitive processes.
Lecithin can be found in various food items including soybeans and sunflower seeds but eggs Sunflower seeds and peanuts also contain lecithin. Due to its excellent emulsifying abilities, Lecithin has long been used as an ingredient in the cosmetic and food industries. It helps maintain the stability and consistency of products like mayonnaise, chocolate, and margarine.
Beyond its many industrial uses, lecithin is being studied for potential health advantages. It is believed to support brain function, liver health, and cholesterol management, although the scientific evidence for some of these claims is still being explored.
Lecithin is a versatile and important compound that plays significant roles in both biological and industrial contexts. Its properties as an emulsifier and its potential health benefits make it a valuable component in various products and formulations.
Importance and relevance of distinguishing between Lectin and Lecithin
Lecithin and Lectin must be distinguished for many reasons outlined below, among them being:
1. Health Implications: Lecithin and lecithin both exert differing impacts on human health. Lectins found in plant foods have been associated with adverse health consequences, including digestive distress and possible links to autoimmune conditions. Identifying lectin-rich foods and understanding their impact on the body is essential for individuals with specific health concerns or sensitivities.
2. Nutritional Benefits of Lecithin: Lecithin is an essential phospholipid component necessary for life that plays an integral part in various Biochemical reactions and functions. Cell membrane lipids play an integral part in cell function and play key roles in processes including emulsification, metabolism of lipids, and brain functioning.
Informing themselves of the significance and health benefits associated with lecithin can aid individuals in making educated choices regarding their diet to optimize overall wellness.
3. Dietary Decisions: Understanding the difference between lecithin and lectin is crucial to make informed dietary choices that support overall wellness. Health may prompt some to avoid lecithin-rich food products; while others may include these food items for optimal performance. Being aware of the differences allows individuals to tailor their diets to their specific health goals and needs.
4. Industries Utilizing Lecithin: Lecithin has long been employed across various fields such as Pharmaceuticals, food processing, and cosmetics. Understanding the properties and applications of lecithin helps industries optimize its use and explore new possibilities for its integration into products.
5. Misinformation and Trends: The distinction between lectin and lecithin is critical in combating misinformation and trends surrounding these substances. Misleading dietary advice, such as the “lectin-free” diet trend, can lead to restrictive eating patterns and potential nutrient deficiencies. Proper education about lectin and lecithin can help individuals make balanced choices and avoid unnecessary dietary restrictions.
6. Safety Considerations: Knowing the differences between lectin and lecithin is crucial for assessing their safety profiles. Although lecithin is generally safe and well tolerated by most, lectins could pose health concerns or sensitivities to certain individuals. Knowing the risks and advantages associated with each substance can assist people in making informed choices regarding its usage.
Reducing lecithin and lectin intake is critical to optimizing overall wellness and health. It allows individuals to make informed dietary choices, supports industries in optimizing product formulations, and helps combat misinformation surrounding these substances. Being aware of the distinct properties, functions, and health implications of lectin and lecithin enables individuals to adopt a balanced and evidence-based approach to nutrition and lifestyle.
Difference Between Lectin and Lecithin
Chemical Composition and Structure
The chemical composition of lecithin and lectin vary, due to their distinct molecular structures:
1. Lectin:
- Lectins are glycoproteins or proteins composed of amino acids connected with each other by carbs molecules, making up their structure.
- The amino acid sequence and arrangement determine the specific three-dimensional shape of the lectin, which allows it to recognize and bind to specific carbohydrate structures in cells and tissues.
- The carbohydrate-binding domain of lectins is essential for their biological functions, as it allows them to interact selectively with carbohydrates present on cell surfaces.
2. Lecithin:
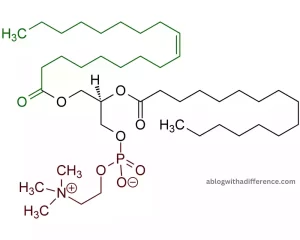
- Lecithin is an example of a phospholipid. As part of its class of lipids (also called fats), it plays an integral part in body functions.
- Lecithin has an intricate structure composed of two chains of hydrophobic fatty acids (hydrophilic tails) linked by three carbon alcohol chains and linked together with Glycerol backbone by three Carbon Alcohol chains which in turn connect phosphate and Choline groups (hydrophilic heads).
- This unique structure imparts amphiphilic properties to lecithin, meaning it has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions within its molecule.
- Lecithin has two hydrophilic heads which attract water while its hydrophobic tails repel it. Lecithin has the unique property to act as an emulsifier and stabilize mixtures containing oil and water.
Lectins are proteins or glycoproteins with a carbohydrate-binding domain, enabling them to selectively interact with specific carbohydrate structures. Lecithin is an amphiphilic phospholipid with Hydrophilic tails and Hydrophobic heads, providing it with the flexibility needed for use as an emulsifier while playing an essential role in cell membrane structure. These distinct chemical compositions and structures underlie the diverse functions and biological roles of lectin and lecithin in different contexts.
Biological Interactions
Biological interactions involving lectins and lecithin are distinct due to their different molecular properties and functions:
1. Biological Interactions of Lectins:
- Lectins are proteins or glycoproteins that can interact with specific carbohydrate structures on the surface of cells and tissues. This interaction is highly specific, and lectins can recognize and bind to certain sugar molecules, such as glucose or mannose.
- Lectins play a vital role in defense against pathogens and predators. When insects or animals consume plant parts containing lectins, the lectins may interfere with their digestion, cause cell agglutination (clumping), or induce other adverse effects, making the consumed plant less palatable or even toxic to the predator.
- Humans use lectins to interact with cells in their digestive tract and produce different effects depending on which lectin they use and individual sensitivities. Some lectins can bind to the lining of the gut, potentially leading to irritation and inflammation in susceptible individuals. Remember to remain mindful that there may be certain lectins that could pose potential threats, with effects varying according to each human’s specific health status.
2. Biological Interactions of Lecithin:
- Lecithin is an amphiphilic, phospholipid. In other words, it acts like an amphiphilic liquid. Its hydrophobic tails interact with other lipids, while its hydrophilic head interacts with water molecules.
- Lecithin plays an essential part in building up cell membrane structure. Lipids comprise the bulk of a cell’s bilayer of lipids that provides insulation between its interior and external environments. The hydrophobic tails of lecithin face inward, shielded from the surrounding water, while the hydrophilic heads face outward, interacting with the aqueous environment.
- Lecithin’s emulsifying properties are also utilized in various biological processes, including digestion. Bile is an essential digestive agent made up of lecithin that aids the body by breaking up fat molecules into smaller droplets that aid with digestion and absorption.
While lectins and lecithin have different biological interactions, it’s important to note that both play significant roles in living organisms. Lectins have essential functions in plants’ defense mechanisms and may have complex effects on human health depending on the specific lectin and individual factors. Lecithin’s role in cell membranes and emulsification contributes to maintaining cellular structure and facilitating various physiological processes, including digestion.
Understanding the distinct interactions between lecithin and lectins is paramount to understanding their significance in biological systems as well as their potential benefits to well-being and health.
Health Implications
Health effects associated with lecithins and their derivatives vary based on individual susceptibilities as well as diet habits and overall well-being.
Health Implications of Lectins:
1. Digestive Issues: Some individuals may experience digestive discomfort, such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea, after consuming foods high in certain types of lectins. Lectins can bind to the lining of the gut, potentially leading to irritation and inflammation in susceptible individuals.
2. Lectin Sensitivity: Some people may be more sensitive to lectins, and consumption of lectin-rich foods may exacerbate existing gastrointestinal conditions or lead to symptoms like joint pain and fatigue.
3. Potential Links to Autoimmune Conditions: Some researchers propose that lectins may play a role in triggering or worsening autoimmune conditions by promoting inflammation and altering gut permeability. Further research should be undertaken to better comprehend the mechanism involved.
4. “Lectin-Free” Diet Trend: The belief that a “lectin-free” diet can improve health has gained popularity, but it is essential to approach such restrictive diets with caution. Eliminating entire food groups may lead to nutrient deficiencies and may not be necessary for most individuals.
Health Implications of Lecithin:
1. Brain Health and Cognitive Function: Lecithin can improve brain health and functionality lecithin is an abundant source of choline, an essential precursor for acetylcholine Neurotransmission which regulates memory formation. Adequate choline intake through lecithin-rich foods or supplements may support brain health.
2. Liver Health: Lecithin’s role in fat metabolism may support liver health by aiding in the transport and breakdown of fats in the liver.
3. Cardiovascular Health: Recent reports indicate lecithin supplementation could have an overall beneficial impact on cholesterol levels by decreasing LDL (or “bad”) and increasing HDL (“good”).
4. Skin Health: Lecithin is an integral component in Skincare products due to its ability to both hydrate and moisturize skin for an improved complexion.
General Considerations:
1. Individual Sensitivities: As with any food component, individuals may have varying sensitivities to lectins and lecithin. Consciously monitoring how certain foods impact your body and seeking medical advice should any adverse reactions occur are of vital importance.
2. Balanced Diets: For improved overall well-being and health, adopting a well-balanced diet that encompasses various foods and nutrients may be more appropriate to achieve total well-being and greater well-being.
3. Moderation and Variety: Moderation is key when consuming any substance. Including a variety of foods in the diet, including lectin-containing plant foods and sources of lecithin, can contribute to a diverse and nutritious eating pattern.
4. Individualized Approach: Individuals who have specific health or dietary concerns or allergies should seek advice from registered dietitians and healthcare experts to tailor their diets according to individual requirements.
Knowledge of lectin and lecithin effects may assist people in making well-informed choices regarding diet and nutrition, leading to healthier lifestyles and practices. As with most aspects of health, every individual responds differently; thus it is wise to consult a healthcare professional before making significant dietary or supplement changes on one’s own.
Consumption and Safety Considerations
Consumption and safety considerations regarding lectins and lecithin are essential to ensure a balanced and healthy diet.
Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Consumption of Lectins:
1. Variety and Moderation: While certain lectins may cause health concerns, most foods that contain them contribute to a balanced and healthful diet and offer many additional advantages for overall well-being. Consuming a wide variety of foods and preparing them using various cooking methods can help reduce lectin content and minimize potential adverse effects.
2. Cooking and Processing: Cooking, soaking, fermenting, and sprouting certain lectin-rich foods can reduce lectin content and increase their digestibility. For example, boiling legumes thoroughly can significantly reduce lectin levels, making them safer to consume.
3. Individual Sensitivities: Pay attention to how your body responds to specific foods. Some individuals may be more sensitive to lectins and may need to limit or avoid certain foods to manage digestive discomfort or other symptoms.
4. Balanced Diet: Instead of restricting yourself from all foods containing lectins, consider opting for an energy-boosting diet with many nutrient-rich options like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources like poultry.
Consumption of Lecithin:
1. Dietary Sources: Lecithin can be found in various food products, including eggs and their yolks Sunflower seeds, and animal tissues. By including these food items in your diet, they will serve as natural sources of lecithin.
2. Supplements: Lecithin supplements can be easily obtained, yet taking them with caution and as per instructions can be challenging. Before embarking on any supplement regimen, seek professional guidance to ascertain if it fits with and supports your unique health requirements.
3. Allergies and Sensitivities: Individuals with allergies to soy or eggs should avoid lecithin derived from these sources. There are other sources of Lecithin such as sunflower lecithin that are suitable for people who are sensitive to egg or soy allergies.
4. Recommended Doses for Lecithin Supplements: When taking lecithin-containing supplements, please follow the recommended dosage recommendations on their label or as advised by a Health practitioner. Excessive supplementation may lead to unwanted side effects.
General Safety Considerations:
1. Individual Variability: Each person’s response to lectins and lecithin can differ based on factors such as genetics, overall health, and individual sensitivities. Be mindful of your body and consult a medical expert if there are concerns.
2. Allergies and Medical Conditions: Before making major dietary or supplement changes or adding new supplements, always consult with a healthcare practitioner first. This could prevent potential allergies, health conditions, or the addition of supplements being caused by allergies or medical issues.
3. Balanced Diet: Make sure to consume an energy-boosting and well-rounded diet consisting of foods packed with vital nutrients for optimal body functioning. Doing this will ensure that all essential nutrition reaches you!
4. Registered Dietitian: For customized diet advice and assistance in meeting health goals, speak to an accredited dietitian. He or she can tailor an appropriate meal plan and diet specifically tailored for you and your specific requirements and goals.
People can make informed choices regarding their diet that support both their own physical wellbeing and general well-being if they understand these aspects of consumption and safety.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between Lecithin and Lectin and their health implications are vitally important to make informed diet choices and promote overall well-being. Lectins, as proteins or glycoproteins, have specific interactions with carbohydrate structures and can have diverse effects on human health, from potential digestive issues to connections with certain autoimmune conditions. Individual sensitivities to lectins may vary, making moderation and variety important in the diet.
Lecithin, on the other hand, is an essential phospholipid that plays an integral part in cell Membrane structure emulsification and metabolism of lipids. It offers potential benefits for brain health, liver function, and cardiovascular health. Lecithin-rich foods and supplements could provide an energetic boost when selected according to individual needs.
When considering the consumption of lectins, it is essential to focus on preparation methods and cooking techniques that reduce lectin content and enhance digestibility.