Hydrocracking and Hydrotreating are two vital processes that play a crucial role in transforming crude oil into valuable end products. These processes are employed to enhance the quality of refined products, improve their properties, and comply with stringent environmental regulations. This article delves into the intricacies of hydrocracking and hydrotreating, exploring their differences, advantages, disadvantages, and future trends in the refining industry.
Definition of Hydrocracking and Hydrotreating
Hydrocracking: Hydrocracking is an oil industry refinery process utilized to convert high-boiling, heavy crude oils, and hydrocarbon feedstocks to lighter products with lower boiling points. Use of hydrogen gas (H2) and an advanced catalyst operating under pressure and temperature to break apart large hydrocarbon molecules into more valuable ones.
This process has proven immensely efficient in producing fuels with lower sulfur contents such as diesel, gasoline, and jet fuel; further providing necessary feedstocks for petrochemical manufacturing processes. Hydrocracking is often employed to upgrade and maximize the yield of valuable products from heavier, less desirable crude oil fractions, thereby enhancing the overall refining efficiency and product quality.
Hydrotreating: Hydrotreating, also referred to as hydrogenation or hydro refining, is an integral refining step utilized by the oil industry to increase feedstock quality and enhance performance. In this process, hydrogen gas (H2) and a catalyst are used to remove impurities and undesirable components from crude oil fractions or other hydrocarbon streams.
The catalyst facilitates chemical reactions between the hydrogen and the feedstock, resulting in the conversion or removal of impurities such as sulfur, nitrogen, and metals.
Hydrotreating operates at moderate to high temperatures and pressures to ensure effective and selective removal of contaminants. By reducing the levels of sulfur, nitrogen, and other heteroatoms, hydrotreating produces cleaner and more environmentally friendly fuels and feedstocks. It is particularly important for meeting stringent environmental regulations and improving the performance and longevity of downstream refining processes, such as catalytic cracking and hydrocracking.
The primary products of hydrotreating are cleaner versions of traditional petroleum products, such as ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) and low-sulfur gasoline, which have reduced emissions and lower environmental impact. Hydrotreating enhances the stability and quality of feedstocks used in further refining processes, leading to higher yields of valuable products and improved overall refinery efficiency.
Importance of these processes in the petroleum industry
Hydrocracking and hydrotreating processes play an essential part of petroleum processing and refinery operations for various reasons, and should never be underestimated as integral processes in an organization’s business operations.
1. Product Diversification: Hydrocracking enables the conversion of heavy and lower-value crude oil fractions into lighter, high-value products such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. This process allows refineries to maximize the production of more valuable products from feedstocks that would otherwise be less desirable, enhancing product diversification and meeting market demands for various refined products.
2. Clean Fuel Production: Both hydrocracking and hydrotreating contribute to the production of cleaner fuels with reduced sulfur, nitrogen, and other harmful impurities. By complying with stringent environmental regulations that mandate lower sulfur content in transportation fuels, these processes aid in reducing emissions of harmful pollutants and improving air quality.
3. Upgrading Feedstocks: Hydrotreating is essential for improving the quality of crude oil or other feedstocks by removing sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen-containing compounds. By upgrading the feedstocks, it enhances their suitability for further processing in other refining units, thereby optimizing the overall refining efficiency.
4. Environmental Compliance: As environmental concerns and regulations become more stringent, hydrocracking and hydrotreating processes are vital in reducing the environmental impact of petroleum refining. The production of cleaner fuels through these processes helps in mitigating air pollution and contributes to overall sustainability efforts.
5. Catalyst Protection: Both processes help protect downstream refining units and catalysts by removing impurities that can poison or deactivate them. This ensures the longevity and effectiveness of catalysts used in other refining processes, resulting in improved overall refinery efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
6. Petrochemical Feedstock Production: Hydrocracking is an efficient means of producing fuels for petrochemical production, an integral component of many manufactured goods such as plastics, solvents, and synthetic materials as well as lubricants and contributing significantly to the expansion of the industry.
7. Economic Benefits: By increasing the production of high-value products and complying with market demands for cleaner fuels, hydrocracking and hydrotreating processes can lead to higher refinery margins and greater profitability for petroleum companies.
8. Energy Security: These methods help maximize crude oil resources by converting feedstocks of lower value into products of greater worth, thus improving energy security by decreasing import dependence while simultaneously increasing domestic production of refined products.
The importance of hydrocracking and hydrotreating lies in their contributions to refining efficiency, cleaner fuel production, environmental compliance, and economic viability in the petroleum industry. These processes allow refineries to meet market demands, adhere to strict environmental standards, and maximize the value of their feedstocks, making them essential for the modern refining landscape.
What is Hydrocracking?
Hydrocracking is an oil refinery process utilized to convert heavy, high-boiling crude oils and hydrocarbon feedstocks to lighter products with reduced boiling points. Hydrogen (H2) gas and an H2-based catalyst used under high pressure and temperature conditions are employed to break apart large complex hydrocarbon molecules into more valuable smaller ones, providing maximum conversion efficiency and maximum profits.
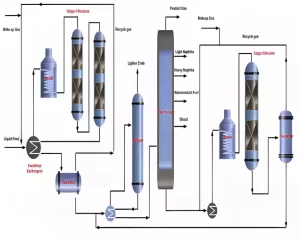
The key objectives of hydrocracking are:
1. Conversion: Heavy hydrocarbons such as long-chain paraffin aromatics and other complex molecules into lighter more valuable products like gasoline jet fuel diesel and other petrochemical feedstocks.
2. Desulfurization: Elimination of sulfur-containing compounds from feedstocks to produce low-sulfur products. This is particularly important to meet stringent environmental regulations that limit sulfur content in transportation fuels.
3. Hydrogenation: To add hydrogen atoms to unsaturated hydrocarbons, such as olefins and aromatics, to saturate them, thus improving product quality and stability.
The hydrocracking process takes place in a reactor vessel, where the feedstock is mixed with hydrogen and passed over a suitable catalyst bed. These hydrogen molecules break apart the chemical bonds found within heavy hydrocarbons to form lighter molecules as well as hydrogen sulfur (H2S) as an unintended by-product.
Hydrocracking is known for its ability to produce high-quality, clean-burning fuels and valuable petrochemical feedstocks. It is commonly used in modern refineries to upgrade and maximize the yield of valuable products from heavier crude oil fractions, thus enhancing overall refining efficiency and product quality. Help meet the increasing demand for eco-friendly fuels by improving air quality.
What is Hydrotreating?
Hydrotreating or Hydrodesulfurization (HDS), is an oil industry process designed to remove impurities such as sulfur from crude oil and various hydrocarbon fuel stocks. Hydrotreating feedstock aims to enhance its quality by eliminating undesirable elements like nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen compounds that could have negative consequences for engine performance, the environment, and downstream catalysts.
The hydrotreating process involves the introduction of hydrogen gas (H2) and the use of a specialized catalyst at elevated temperature and pressure conditions. These reactions affect sulfur nitrogen sulfur and oxygen-rich substances within feedstocks to alter them chemically and produce changes.
Through this reaction, sulfur is converted to hydrogen sulfur sulfide (H2S) while nitrogen becomes ammonia (NH3) while oxygen changes into water (H2O). These reaction products are easier to separate and remove from the hydrocarbon stream, effectively reducing the impurities in the final product.
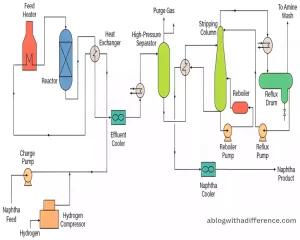
The key objectives of hydrotreating are:
1. Desulfurization: To reduce the sulfur content in the feedstock, leading to the production of cleaner fuels with lower sulfur levels. This is essential to comply with environmental regulations that impose strict limits on sulfur content in transportation fuels.
2. Denitrogenation: To decrease the nitrogen content in the feedstock, which is important for reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions during combustion and enhancing the quality of the final product.
3. Deoxygenation: To remove oxygen-containing compounds, such as organic acids and carbonyl compounds, which can negatively affect product stability and storage.
Hydrotreating is an integral step in refining, helping produce more cost-efficient low-sulfur fuels such as ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) and gasoline with reduced sulfur. It also protects downstream refining units and catalysts from poisoning or deactivation by the impurities present in the feedstock, thereby improving the overall efficiency and reliability of the refining process. Hydrotreating plays a significant role in meeting environmental standards and ensuring the production of high-quality, environmentally friendly fuels.
Key Differences Between Hydrocracking and Hydrotreating
Hydrocracking and hydrotreating are both important refining processes used in the petroleum industry, but they have distinct differences in their objectives, reaction mechanisms, feedstock requirements, and product outcomes. Here is the primary difference between hydrocracking and treating:
1. Objectives:
- Hydrocracking: Hydrocracking’s primary objective is the conversion of high-boiling crude oil and other hydrocarbon feedstocks to lighter more valuable goods like diesel, gasoline jet fuel, or even petrochemical feedstocks. It focuses on maximizing the production of high-value products.
- Hydrotreating: Hydrotreating’s primary objective is the removal of impurities such as sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen compounds found in crude oil or other feedstocks. The targeted goals of this initiative include developing more cost-efficient and less sulfurous fuels while simultaneously improving feedstock quality overall.
2. Reaction Mechanisms:
- Hydrocracking: Hydrocracking involves breaking the chemical bonds in large, complex hydrocarbon molecules through the use of hydrogen gas and a specialized catalyst. This results in the formation of smaller, lighter hydrocarbon molecules.
- Hydrotreating: Hydrotreating involves the introduction of hydrogen gas and a specialized catalyst to react with and remove sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen-containing compounds. Impurities can be converted to hydrogen sulfur (H2S), ammonia (NH3), and water as byproducts.
3. Feedstock Requirements:
- Hydrocracking: Hydrocracking typically uses heavier and more complex feedstocks, such as vacuum gas oils, heavy gas oils, and residues, which have higher molecular weights and boiling points.
- Hydrotreating: Hydrotreating can work with a broader range of feedstocks, including lighter fractions, distillates, and even some intermediate products. This program’s objective is to enhance feedstock quality by decreasing impurity levels across its molecular mass range, regardless of material source or particle size.
4. Product Outcomes:
- Hydrocracking: The products of hydrocracking are lighter, more valuable fuels and petrochemical feedstocks, such as gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and base oils. Producing lighter gases such as LPG (liquefied petroleum gas).
- Hydrotreating: Hydrotreating can produce cleaner and lower sulfur fuels such as ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) or gasoline with reduced sulfur levels. The process focuses on reducing the sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen content in the feedstock.
5. Process Conditions:
- Hydrocracking: Hydrocracking requires more severe process conditions, including higher temperatures and pressures, to achieve the desired cracking reactions.
- Hydrotreating: Hydrotreating operates at lower temperatures and pressures compared to hydrocracking, as its primary purpose is to facilitate the removal of impurities rather than extensive cracking reactions.
Hydrocracking focuses on converting heavy feedstocks into lighter, more valuable products, while hydrotreating aims to remove impurities and produce cleaner fuels. The two processes have different feedstock requirements, and product outcomes, and operate under distinct process conditions to achieve their respective objectives in the refining industry.
Future Trends in Hydrocracking and Hydrotreating Technologies
As the petroleum industry evolves and strives to meet growing energy demands while addressing environmental concerns, several future trends are expected in hydrocracking and hydrotreating technologies:
1. Advanced Catalyst Development: Research and development efforts will focus on creating more efficient and selective catalysts for both hydrocracking and hydrotreating processes. Improved catalysts will enhance product yields, increase conversion rates, and reduce energy consumption, ultimately leading to more sustainable and cost-effective operations.
2. Integration of Renewable Hydrogen: To reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance sustainability, refineries may increasingly integrate renewable hydrogen sources, such as electrolysis-powered hydrogen, into hydrocracking and hydrotreating processes. The use of renewable hydrogen can lower the carbon footprint of these processes and contribute to the overall decarbonization of the petroleum industry.
3. Biogenic Feedstocks: Refineries may explore the use of biogenic feedstocks, such as bio-oils or waste-derived hydrocarbons, in hydrocracking and hydrotreating. Integrating renewable feedstocks can offer greater feedstock flexibility and promote the production of biofuels and renewable chemicals, contributing to a more circular and bio-based economy.
4. Increased Focus on Hydrotreating: As environmental regulations continue to tighten, refineries may place greater emphasis on hydrotreating technologies. Hydrotreating will become crucial in producing ultra-low sulfur fuels and other environmentally friendly products, ensuring compliance with strict emissions standards.
5. Residue Conversion: Future hydrocracking technologies may be optimized for converting heavy residues and unconventional feedstocks, such as heavy oils, bitumen, and oil sands, into lighter, more valuable products. Innovative hydrocracking processes will be essential to unlock the full potential of these abundant but challenging feedstocks.
6. Hydrocracking for Chemical Production: Hydrocracking may be increasingly used to produce petrochemical feedstocks, as demand for chemicals and high-value derivatives continues to rise. Tailoring hydrocracking units for targeted chemical production can provide refineries with a competitive edge in the growing petrochemical market.
7. Process Intensification: Future trends in hydrocracking and hydrotreating will likely focus on process intensification, which involves increasing process efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing environmental impact. Integrating process intensification concepts, such as modular designs and enhanced heat integration, can lead to more compact and sustainable refining operations.
8. Digitalization and Automation: The integration of digital technologies and advanced process control systems will optimize hydrocracking and hydrotreating operations. Real-time monitoring, data analytics, and predictive maintenance will improve process reliability, reduce downtime, and enhance safety and efficiency.
9. Electrification: The petroleum industry may explore partial or complete electrification of certain refinery processes, including hydrogen generation and compression, to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and further decrease emissions.
Future developments of hydrocracking and hydrotreating technologies should aim to optimize efficiency while decreasing the environmental footprint, adapting to changes in energy markets, and taking into account evolving energy sector needs. Continuous innovation, research, and collaboration between refineries, research institutions, and technology providers will drive these advancements, paving the way for a more sustainable and resilient petroleum refining sector.
Applications of Hydrocracking and Hydrotreating
Hydrocracking and hydrotreating are essential refining processes with diverse applications in the petroleum industry. Here are some key applications of each process:
Applications of Hydrocracking:
1. Production of Cleaner Fuels: Hydrocracking technology has long been utilized as an eco-friendly means to produce cleaner fuels such as gasoline diesel jet and fuel; with fewer sulfur emissions and improved combustion. Cleaner fuels could help decrease emission levels such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx), in addition to particulate matter produced during combustion – improving both air quality and health benefits simultaneously.
2. Petrochemical Feedstock Production: Hydrocracking can be tailored to produce valuable petrochemical feedstocks, including light olefins (ethylene and propylene) and aromatics (benzene, toluene, and xylene). These feedstocks are indispensable components in various industries such as rubber manufacturing, plastics processing, and synthetic fibers production as well as detergent production.
3. Upgrading Heavy Residues: Hydrocracking is used to convert heavy and less valuable residues, such as vacuum gas oils and residues from crude oil refining, into lighter and higher-value products. This helps maximize the utilization of crude oil resources and improves the overall efficiency of the refining process.
4. Conversion of Unconventional Feedstocks: Hydrocracking can be adapted to convert unconventional feedstocks, such as heavy oils, bitumen, and oil sands, into lighter products suitable for downstream processing and market demand.
Applications of Hydrotreating:
1. Desulfurization of Fuels: Hydrotreating Fuels Hydrotreating can help lower the amount of sulfur present in fuels like diesel and gasoline to meet strict environmental standards requiring low sulfur fuel content. This process helps refineries comply with emissions standards and produce ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) and low-sulfur gasoline.
2. Denitrogenation and Deoxygenation: Hydrotreating removes nitrogen and oxygen-containing compounds from feedstocks to enhance fuel stability and reduce emissions during combustion. It plays a crucial role in improving the overall quality and environmental performance of fuels.
3. Improving Feedstock Quality: Hydrotreating is used to upgrade various feedstocks, including straight-run distillates, cracked naphthas, and even intermediate products, to make them suitable for further processing in other refining units. By removing impurities, hydrotreating ensures the smooth operation of downstream processes and protects catalysts from deactivation.
4. Refinery Integration: Hydrotreating is a versatile process that can be integrated into various refinery units to achieve specific objectives. It is often utilized in combination with other refining processes, such as catalytic reforming, to optimize the overall refining efficiency and product slate.
Both hydrocracking and hydrotreating are critical in refining operations for producing cleaner fuels, meeting environmental regulations, and maximizing the value of crude oil resources. Refineries may implement one or both processes depending on their specific refining objectives, market demands, and regulatory requirements.
By using these processes strategically, refineries can enhance their competitiveness, environmental performance, and overall sustainability in the ever-evolving energy landscape.
Conclusion
Hydrocracking and hydrotreating are essential refining processes in the petroleum industry, each serving distinct purposes and contributing to the production of high-quality fuels and valuable petrochemical feedstocks.
Hydrocracking excels in converting heavy and complex hydrocarbon feedstocks into lighter, more valuable products, such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. It significantly enhances product quality, reduces sulfur content, and increases the overall yield of valuable products. However, it requires higher capital investment, operates under more severe conditions, and may lead to increased greenhouse gas emissions.
Hydrotreating, on the other hand, is an efficient means of improving feedstock’s quality by eliminating impurities like nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen-containing materials that diminish its value. It results in cleaner, low-sulfur fuels that meet strict environmental regulations. While hydrotreating may not offer extensive product diversification like hydrocracking, it is cost-effective, environmentally beneficial, and plays a vital role in ensuring the quality of the final products.