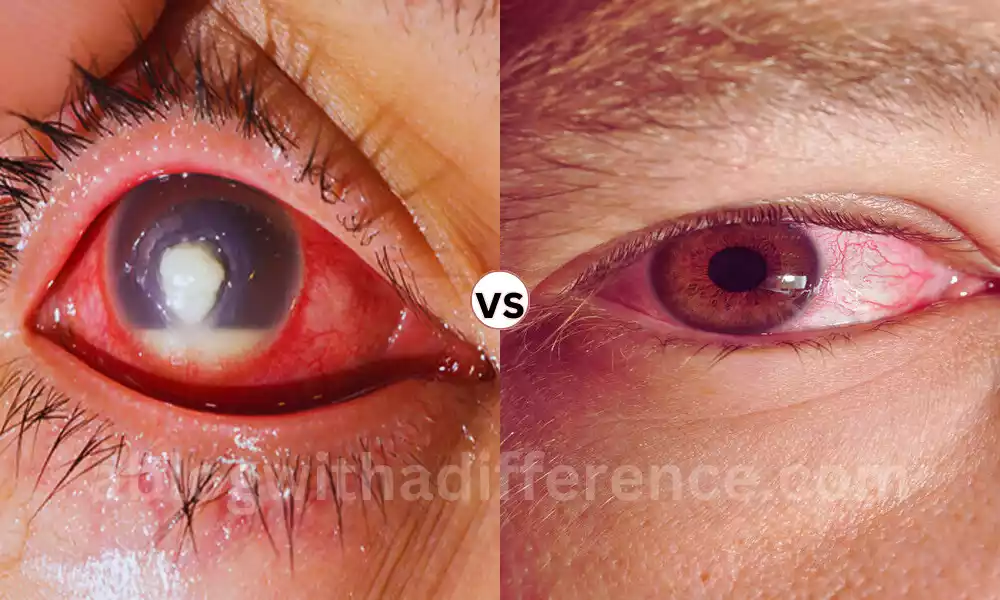
What is the Difference Between Keratitis and Conjunctivitis
Eye infections are conditions where harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, invade the eye’s structures, causing inflammation and potential damage. These infections can affect various parts of the eye, including the conjunctiva, cornea, and surrounding tissues.
Common symptoms include redness, itching, discharge, and discomfort. Prompt diagnosis and treatment by a healthcare professional are essential to prevent complications and preserve eye health. Proper hygiene, avoiding irritants, and regular eye check-ups contribute to the prevention of eye infections.
What is Keratitis?
Keratitis is an eye condition that is characterized by the inflammation or irritation of the cornea, which is the transparent dome-shaped outer layer that covers part of the cornea’s front. It may be caused by a variety of reasons, such as infections (viral or fungal), bacterial or parasitic) as well as injuries, underlying illnesses, and prolonged wearing of contact lenses.
The signs of keratitis could include eye redness as well as pain or discomfort within the eyes, light sensitivity (photophobia) fuzzy vision, excess tears and discharge of the eyes, feeling of something being inside the eye, and a feeling of watering or tears of the eye affected.
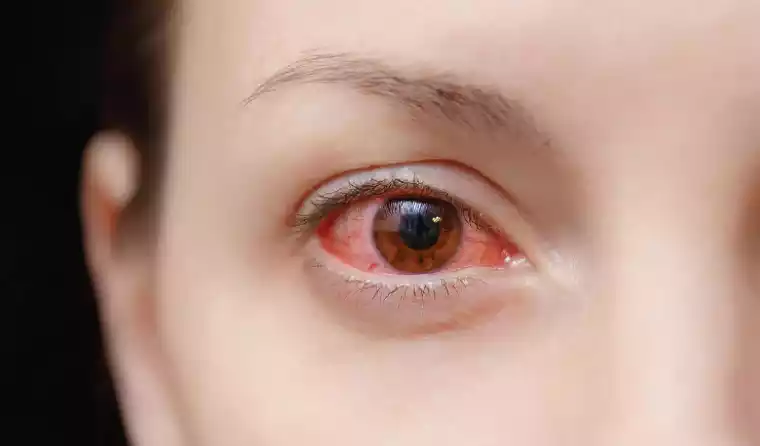
Treatment for keratitis usually depends on the causes. Fungal or bacterial keratitis may require an antibiotic or antifungal eye drops or Ointments. Keratitis caused by viral infection can be treated by taking antiviral medicines. If the condition is severe or vision is in danger the need for hospitalization or more aggressive treatments such as oral medication or surgery may be required.
A prompt diagnosis and the right treatment are essential to avoid complications that could result in loss of vision. If anyone suspects that they may have Keratitis or has symptoms similar to it, seeking prompt medical assistance from an eye health expert is vital to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Delving into Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis commonly referred to by the name of “pink eye,” refers to swelling or irritation of the conjunctiva – the thin transparent layer of tissues that covers the white area of the eye. It also lines the surface of the lids. It can be present in both eyes. It is characterized by symptoms like irritation, itching, redness as well and excessive tear production. an edema that may cause the eyelids to stay together, especially after sleeping.
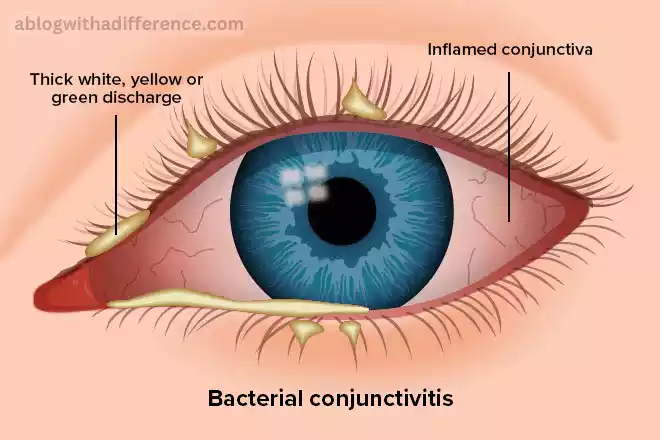
There are a variety of types of conjunctivitis.
- Viral conjunctivitis: is caused by a virus that is like the common cold, but highly contagious. It is often spread through coughing, sneezing or even touching surfaces that are contaminated.
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis: The condition is caused by bacteria. It may result from contact with objects that are contaminated as well as poor hygiene or incorrect use of contact lenses. It can also be transmitted.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: Caused by allergens such as dust mites, pollen, animal dander, or other chemicals. It’s not contagious, but can trigger symptoms such as itching, redness and even tearing.
- Chemical Conjunctivitis: It is caused by exposure to irritants such as chemical fumes, chemicals, or chlorine in swimming pools. This kind of infection isn’t contagious.
The treatment for conjunctivitis is different based on the underlying cause
- Viral Conjunctivitis: Usually, it heals in several days or two weeks. Ice packs and artificial tears can ease symptoms.
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis: Eye drops with antibiotics or ointments are often used to eliminate the infection. The full course of treatment is crucial to avoid any recurrence.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: Eye drops containing antihistamines or oral medication can offer relief. It is essential to avoid allergens.
- Chemical Conjunctivitis: The immediate rinsing of the eye with clear water is required. In severe cases, it is possible to require medical care.
It’s recommended to talk with a medical professional or an eye specialist in the event that someone suspects conjunctivitis. This is especially true if there’s discomfort, changes in vision sensitivity, or irritation to light to ensure a proper diagnosis and treatment. Practicing good hygiene, avoiding touching eyes with dirty hands, and avoiding sharing things like makeup or towels will help to prevent the dispersal of conjunctivitis.
Key comparison chart
Below is a key comparison chart highlighting the differences between Keratitis and Conjunctivitis:
| Aspect | Keratitis | Conjunctivitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflammation of the cornea | Inflammation of the conjunctiva |
| Affected Structure | Cornea | Conjunctiva (thin, transparent layer covering the white part of the eye and inner eyelids) |
| Causes | Infections (bacterial, viral, fungal, parasitic), injuries, underlying health conditions | Viral infections, bacterial infections, allergic reactions, irritants |
| Symptoms | Eye pain, redness, sensitivity to light, blurred vision | Redness, itching, tearing, discharge, sensitivity to light |
| Diagnosis | Eye examination, corneal scraping for laboratory analysis | Clinical examination, patient history |
| Treatment | Antibiotic, antiviral, or antifungal eye drops; pain management; rest | Viral: Supportive care; Bacterial: Antibiotic eye drops or ointments; Allergic: Antihistamines or mast cell stabilizers |
| Prevention | Hygiene practices, avoiding irritants, regular eye check-ups | Hygiene practices, avoidance of allergens, proper contact lens care |
| Complications | Corneal scarring, vision impairment | Corneal involvement, chronic discomfort |
| Seeking Medical Attention | Persistent eye pain, redness, changes in vision | Persistent or worsening symptoms, sudden changes in vision |
This chart provides a concise overview of the key distinctions between keratitis and conjunctivitis in terms of causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, complications, and when to seek medical attention.
Similarities of Keratitis and Conjunctivitis
Common Ground: Similarities Between Keratitis and Conjunctivitis
While keratitis and conjunctivitis are distinct eye conditions with different primary sites of inflammation, they share some commonalities in terms of symptoms and the importance of prompt medical attention. Understanding these similarities can aid in recognizing and addressing these eye issues effectively.
Redness and Irritation: Both keratitis and conjunctivitis often manifest with redness in the affected eye. The inflammation in these conditions can cause visible blood vessels, giving the eyes a reddish appearance. Additionally, individuals may experience irritation or discomfort, contributing to the red-eye symptom.
Tearing and Discharge: Excessive tearing and eye discharge are prevalent in both conditions. While the nature of discharge may differ (watery, mucous, or pus-like), the presence of abnormal eye secretions is a shared characteristic. Discharge can affect vision and may lead to discomfort or crusting around the eyes.
Sensitivity to Light: Sensitivity to light, known as photophobia, is a common symptom in both keratitis and conjunctivitis. The inflamed structures in the eyes become more reactive to light, causing discomfort and a desire to avoid well-lit environments.
Risk of Complications: If left untreated, both keratitis and conjunctivitis can lead to complications that may affect vision and overall eye health. Complications can include corneal scarring in keratitis or corneal involvement in severe conjunctivitis cases, highlighting the importance of timely and appropriate medical intervention.
Infectious Causes: While the specific microorganisms causing these conditions may differ, both keratitis and certain types of conjunctivitis (bacterial or viral) can result from infectious agents. Proper diagnosis is crucial to determine the appropriate treatment, whether it involves antibiotics, antivirals, or other therapeutic measures.
Seeking Medical Attention: Persistent or worsening symptoms in either keratitis or conjunctivitis necessitate prompt medical attention. Timely diagnosis and treatment by an eye care professional are vital to prevent complications and ensure a positive outcome.
Recognizing these shared features can assist individuals in identifying potential eye issues early on and seeking timely medical guidance. It underscores the importance of professional care to address these conditions effectively and safeguard eye health.
Impact on Daily Life
Navigating Daily Life with Keratitis and Conjunctivitis: Managing Impact on Vision and Well-being
Both keratitis and conjunctivitis can significantly influence daily life, impacting various aspects of one’s routine and overall well-being. While the specific challenges may differ between the two conditions, managing these impacts requires a combination of proper medical care, lifestyle adjustments, and heightened awareness.
Vision Impairment:
- Keratitis: The cornea’s involvement in keratitis can lead to blurred vision and increased sensitivity to light. Tasks requiring clear eyesight, such as reading or driving, may become challenging.
- Conjunctivitis: While vision impairment is less common in conjunctivitis, the discomfort and tearing associated with the condition can still affect visual acuity.
Discomfort and Irritation:
- Keratitis: Persistent eye pain and discomfort are characteristic symptoms of keratitis, impacting the ability to focus on daily activities.
- Conjunctivitis: Itchy and irritated eyes in conjunctivitis can cause continuous discomfort, making it challenging to concentrate on work or leisure activities.
Social Interactions:
- Keratitis: The visible redness and sensitivity to light may make individuals with keratitis more self-conscious, affecting their comfort in social situations.
- Conjunctivitis: The contagious nature of certain conjunctivitis types can lead to social isolation, as individuals may avoid close contact to prevent spreading the condition.
Work and Productivity:
- Keratitis: Tasks requiring intense focus or prolonged screen time may be hindered by the discomfort and vision issues associated with keratitis.
- Conjunctivitis: Individuals with conjunctivitis, especially if the condition is contagious, may need to take time off work to prevent spreading the infection to colleagues.
Daily Hygiene Practices:
- Keratitis: Individuals with keratitis may need to be cautious about proper hygiene, especially if contact lenses are involved. This includes meticulous lens care and regular handwashing.
- Conjunctivitis: Strict adherence to hygiene practices is essential to prevent the spread of contagious conjunctivitis. This involves avoiding touching the eyes and ensuring proper disposal of tissues or other materials that come into contact with the eyes.
Treatment Regimen:
- Keratitis: Managing keratitis often involves a specific treatment regimen, including the application of eye drops or ointments, which may require consistent and careful administration.
- Conjunctivitis: Depending on the type (viral, bacterial, or allergic), treatment may involve different medications or supportive care. Adhering to the prescribed treatment plan is crucial for effective resolution.
Navigating daily life with keratitis or conjunctivitis involves a combination of self-care practices, medical intervention, and understanding the condition’s impact on various aspects of well-being. Seeking timely medical attention, adopting recommended treatments, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments contribute to a smoother journey toward recovery and maintaining a good quality of life.
Real-life Cases
Real-Life Cases: Navigating Challenges with Keratitis and Conjunctivitis
Understanding the impact of keratitis and conjunctivitis on individuals often becomes more poignant through real-life cases, where these eye conditions can present unique challenges. Here are two distinct scenarios illustrating how these conditions can affect people in their day-to-day lives:
Case 1: Sarah’s Battle with Keratitis
Sarah, a dedicated computer programmer, began experiencing persistent eye pain and sensitivity to light. As her symptoms progressed, she noticed blurred vision affecting her ability to read code and work on intricate programming tasks. Seeking medical attention, she was diagnosed with keratitis, a condition exacerbated by prolonged screen time and inadequate breaks. Sarah had to make significant adjustments to her work routine, incorporating regular breaks, using lubricating eye drops, and wearing specially prescribed contact lenses. Her journey involved not only adhering to a strict treatment plan but also adapting her work environment to minimize eye strain. Sarah’s story emphasizes the impact of keratitis on professional tasks and the need for tailored solutions to maintain productivity.
Case 2: Jake’s Experience with Contagious Conjunctivitis
Jake, a college student, developed red, itchy eyes during exam week. Concerned about spreading the discomfort to his peers, he visited the campus health center, where he was diagnosed with viral conjunctivitis. Jake faced the challenge of navigating social interactions while adhering to a period of isolation to prevent contagion. He had to miss classes and study groups, impacting his academic commitments. Jake’s case highlights the social aspects of conjunctivitis, where the contagious nature of the condition requires individuals to balance their health needs with the responsibility of preventing the spread to others. His experience underscores the importance of communication and understanding among peers and educators during such circumstances.
Key Takeaways from Real-Life Cases:
- Individualized Challenges: The impact of keratitis and conjunctivitis varies based on factors such as profession, lifestyle, and social context. Tailored approaches are essential for effective management.
- Work and Education Adjustments: Both cases demonstrate the need for adjustments in work or academic settings. Whether it’s modifying the work environment or taking temporary breaks, these accommodations are crucial for individuals facing these eye conditions.
- Social Implications: The contagious nature of conjunctivitis highlights the social challenges individuals may encounter. Open communication, understanding, and supportive environments play a vital role in managing the impact on relationships and daily interactions.
- Treatment Adherence: Both cases emphasize the significance of following prescribed treatment plans. Consistency in using medications, adhering to hygiene practices, and seeking follow-up care are essential for a positive outcome.
Real-life cases underscore the multifaceted challenges individuals may encounter when dealing with keratitis and conjunctivitis. By sharing these stories, we gain insights into the importance of personalized care, supportive environments, and the resilience individuals demonstrate in navigating these eye conditions.
The Role of Optometrists
The Vital Role of Optometrists: Guardians of Eye Health
Optometrists play a crucial role in safeguarding and enhancing our vision, contributing significantly to overall eye health. In addition to prescribing glasses and contact lenses, these eye care professionals are essential in the early detection, diagnosis, and management of various eye conditions.
Here’s a brief exploration of the indispensable role optometrists play:
Comprehensive Eye Examinations: Optometrists conduct thorough eye examinations, assessing visual acuity, eye muscle coordination, and the health of the eye structures. These examinations are not only about determining prescriptions for corrective lenses but also about identifying early signs of eye diseases.
Detection of Eye Conditions: Optometrists are trained to identify a wide range of eye conditions, including glaucoma, cataracts, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy. Early detection allows for timely intervention and prevents potential vision loss.
Prescription and Management: Prescribing corrective lenses is just the beginning. Optometrists provide personalized solutions for visual challenges, considering factors like lifestyle and occupational demands. Additionally, they manage and monitor conditions such as astigmatism, myopia, and hyperopia.
Contact Lens Fitting and Management: Optometrists specialize in fitting and managing contact lenses, ensuring the proper fit, comfort, and visual clarity. They guide patients on lens care practices and address any issues related to contact lens use.
Patient Education: Optometrists play a vital role in educating patients about eye health, preventive measures, and lifestyle factors that impact vision. This includes guidance on proper nutrition, eye safety practices, and the importance of regular eye examinations.
Collaboration with Healthcare Providers: Optometrists collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as ophthalmologists and general practitioners, to ensure comprehensive care for patients. They refer individuals to specialists when necessary and contribute to a holistic healthcare approach.
Advocacy for Eye Health: Optometrists advocate for eye health awareness in communities, emphasizing the importance of routine eye examinations for individuals of all ages. Their efforts contribute to early intervention and the prevention of avoidable vision impairment.
Optometrists serve as frontline defenders of our eyesight. Through their expertise, they not only enhance our visual experience but also contribute to the overall health and well-being of individuals. Regular visits to optometrists are a proactive step toward maintaining optimal vision and preventing potential eye issues.
Busting Myths
Myth-Busting: Clarifying Common Misconceptions About Eye Health
Myth: “Wearing Glasses Weakens Your Eyes.”
Reality: Glasses correct vision issues; they don’t weaken eyes. In fact, ignoring necessary prescriptions can strain the eyes and worsen conditions.
Myth: “Reading in Dim Light Damages Your Eyes.”
Reality: While reading in low light may cause eye strain, it doesn’t lead to permanent damage. Adequate lighting reduces eye fatigue.
Myth: “Using Screens Ruins Eyesight.”
Reality: Extended screen time may cause discomfort, but it doesn’t cause permanent damage. Follow the 20-20-20 rule (every 20 minutes, look 20 feet away for 20 seconds) to reduce strain.
Myth: “Eating Carrots Improves Vision.”
Reality: Carrots are rich in vitamin A, important for eye health, but excessive consumption won’t enhance vision. A balanced diet supports overall eye health.
Myth: “Sitting Too Close to the TV Harms Your Eyes.”
Reality: Sitting close doesn’t cause permanent damage. It’s a behavior often seen in children and usually indicates nearsightedness.
Myth: “Only Older Adults Need Eye Exams.”
Reality: Everyone, regardless of age, should have regular eye exams. Many eye conditions are easier to treat when detected early.
Myth: “Rubbing Your Eyes Causes Vision Problems.”
-
- Reality: Occasional rubbing is normal, but excessive rubbing may irritate the eyes. It doesn’t cause long-term vision issues.
Dispelling these myths promotes a better understanding of eye health and encourages proactive measures for maintaining optimal vision.
Eye Care Tips
Quick Eye Care Tips for Optimal Vision:
Regular Eye Exams:
Schedule comprehensive eye exams at least every two years to detect and address potential issues early.
Protective Eyewear:
Wear sunglasses with UV protection outdoors and safety glasses when engaging in activities with potential eye hazards.
Follow the 20-20-20 Rule:
Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds to reduce eye strain during prolonged screen use.
Balanced Diet:
Consume a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, including those beneficial for eye health, such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants.
Hydrate:
Stay adequately hydrated to maintain moisture in the eyes and prevent dryness.
Proper Lighting:
Ensure good lighting when reading or working to reduce eye strain and fatigue.
Regular Breaks:
Take breaks during extended screen use to rest your eyes and prevent computer vision syndrome.
Clean Contact Lenses:
If you wear contact lenses, follow proper cleaning and hygiene practices to prevent infections.
Quit Smoking:
Smoking is linked to various eye conditions. Quitting can reduce the risk of vision impairment.
Stay Active:
-
- Regular physical activity promotes overall health, including eye health.
Incorporating these habits into your routine can contribute to maintaining clear vision and overall eye health.
Children and Eye Infections
Children and Eye Infections: A Quick Guide for Parents
Recognizing Symptoms:
Be vigilant for signs of eye infections in children, including redness, itching, tearing, discharge, light sensitivity, and complaints of pain or discomfort.
Frequent Handwashing:
Teach children the importance of handwashing to prevent the spread of infections. Discourage rubbing or touching the eyes with dirty hands.
Avoiding Sharing Personal Items:
Discourage children from sharing items like towels, pillows, or toys that come into contact with the face and eyes.
Proper Hygiene for Contact Lens Wearers:
If your child wears contact lenses, ensure they follow strict hygiene practices and replace lenses as directed by the eye care professional.
Prompt Medical Attention:
If you suspect an eye infection, seek prompt medical attention. Delayed treatment can lead to complications.
Limiting Screen Time:
Implement reasonable limits on screen time to reduce the risk of computer vision syndrome and eye strain.
Encouraging Outdoor Play:
Outdoor activities can contribute to overall eye health. Sunlight and a change of focus from near to far can benefit visual development.
Balanced Nutrition:
Ensure your child’s diet includes foods rich in eye-friendly nutrients, such as fruits, vegetables, and foods high in omega-3 fatty acids.
Protective Eyewear:
Encourage the use of protective eyewear during activities where there’s a risk of eye injury, such as sports or outdoor play.
Regular Eye Check-ups:
-
- Schedule regular eye examinations for your child, even if there are no apparent issues. Early detection and intervention are crucial for visual development.
Prioritizing eye health in childhood sets the foundation for a lifetime of good vision. By instilling proper hygiene practices, promoting a healthy lifestyle, and addressing eye issues promptly, parents can help ensure their children’s eyes stay clear, comfortable, and free from infections.
Conclusion of Keratitis vs Conjunctivitis
While keratitis and conjunctivitis both involve inflammation of the eye, they are distinct conditions with different affected structures and causes. Keratitis targets the cornea and can result from infections, injuries, or underlying health issues, leading to symptoms like eye pain, redness, and sensitivity to light. Conjunctivitis, on the other hand, affects the conjunctiva and can stem from viral, bacterial, allergic, or irritant causes, presenting symptoms such as redness, itching, tearing, and discharge.
The key to effective management lies in understanding their differences. Keratitis demands careful diagnosis and targeted treatments like antibiotic or antifungal eye drops, while conjunctivitis may require antiviral or antibiotic medications depending on the type. Both conditions underscore the importance of seeking prompt medical attention, adhering to prescribed treatments, and practicing good eye hygiene to prevent complications and promote overall eye health.
FAQs
- Can I use over-the-counter eye drops for both keratitis and conjunctivitis?
- It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
- Is conjunctivitis always contagious?
- While most types of conjunctivitis are contagious, it’s best to seek medical advice to determine the specific nature of the infection.
- Can children wear contact lenses if they have had keratitis or conjunctivitis?
- Consult an eye care specialist to assess whether it’s safe for children to wear contact lenses after recovering from these infections.
- Are there natural remedies for relieving symptoms of keratitis and conjunctivitis?
- While some home remedies may offer relief, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate guidance.
- How often should adults and children have eye check-ups to detect infections early?
- Regular eye check-ups are recommended at least once a year for adults and more frequently for children, especially if