9 Amazing Secret about Hepatomegaly and Fatty Liver
Introduction of Hepatomegaly and Fatty Liver
Hepatomegaly and Fatty Liver can be seen in the fact that it can be described as medically induced due to the liver’s size growing, while it is a medical issue caused by the accumulation of fat that is not stored within the liver.
Hepatomegaly refers to an enlarged liver caused by infections, inflammations, metabolic disorders, or excessive alcohol consumption. Symptoms may include abdominal discomfort. Diagnosis includes physical exams, imaging, blood tests, and treatment options that address its source.
Fatty liver is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat cells within liver tissue. There are two main forms, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD).
NAFLD is often caused by obesity or insulin resistance while excessive alcohol consumption leads to AFLD. Both conditions can lead to inflammation and damage of liver tissue which in turn could progress further into more serious liver conditions.
Diet and exercise play an integral part in managing fatty liver along with medication as well as more advanced surgical options when necessary.
What is Hepatomegaly?
Hepatomegaly, commonly referred to as an enlarged liver, is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal increase in liver size. The liver plays an essential role in our bodies from detoxification, metabolism, and producing bile to detoxifying our system as a whole.
So its abnormal size may signal either an underlying health issue or an overworked liver. Hepatomegaly can be caused by various factors, including infections (hepatitis), inflammatory conditions (like cirrhosis), metabolic disorders such as Hemochromatosis or Wilson’s disease), or chronic alcohol abuse.
When symptoms do appear, they usually involve discomfort or pain in the upper right abdominal region and include physical examination, imaging tests like ultrasound CT or MRI scans, and blood tests to ascertain its source.
Treatment typically includes antiviral drugs anti-inflammatory medicines as well as lifestyle modifications to treat its source.
What is Fatty Liver?
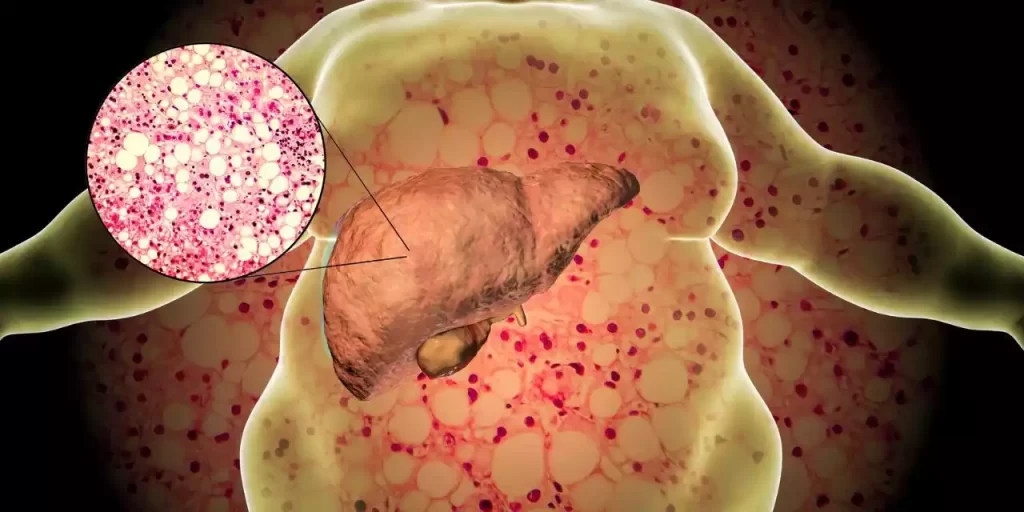
Fatty liver (hepatic steatosis) is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fat within liver cells. This condition is very prevalent and has two primary forms: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD).
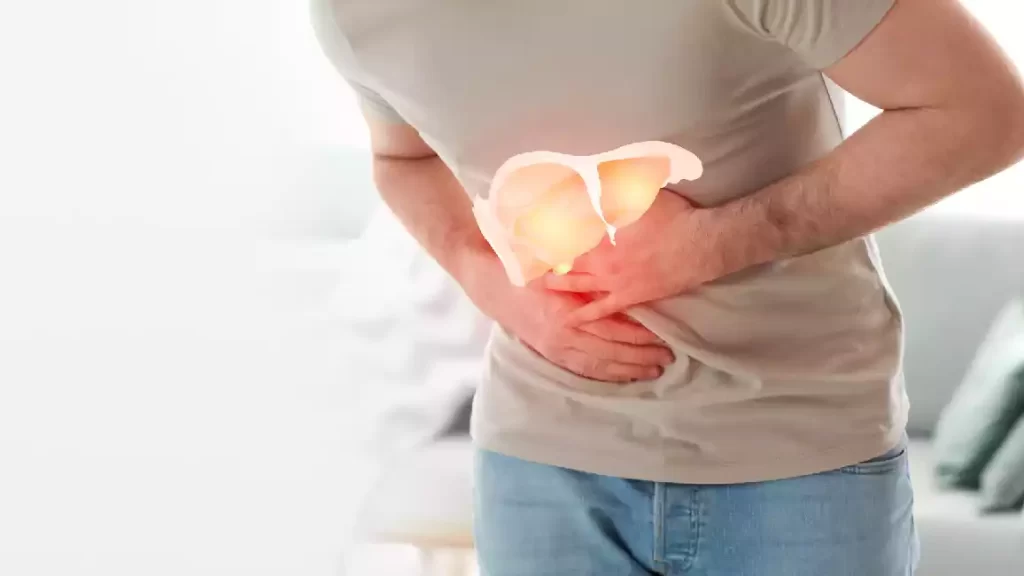
NAFLD is most often caused by lifestyle factors like obesity, insulin resistance, and eating too much dietary fat. It often progresses silently over time and in more serious cases can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), potentially leading to liver inflammation and scarring.
AFLD, on the other hand, is caused by excessive alcohol intake and can result in liver hepatitis or even cirrhosis. Both types of fatty liver can significantly impair liver function and, left unchecked, lead to more serious liver diseases.
Treatment often includes lifestyle modifications like weight loss, eating healthily and regular physical activity medications may be prescribed in advanced cases while surgical intervention might also be necessary regular medical monitoring and early intervention are key elements in effectively treating fatty livers.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Hepatomegaly and Fatty Liver
Hepatomegaly:
- Abdominal discomfort: People living with hepatomegaly often report feeling fullness or discomfort in the upper right quadrant of their abdomen.
- Abdominal pain: Some may experience mild to moderate abdominal discomfort in the liver region.
- Visible abdominal enlargement: In advanced cases of hepatomegaly, abdominal distention or protrusion may occur as the liver expands uncontrollably and expands visibly within.
- Jaundice: An impairment in liver function may cause the yellowing of skin and eyes in more serious cases of jaundice, leading to yellow spots on the skin and eyes.
- Unintentional Weight Loss: Some individuals may experience sudden and unexplained weight loss, usually as the result of Hepatomegaly’s root cause.
- Fatigue: Fatigue and weakness may be symptoms of liver dysfunction.
- Nausea and vomiting: When Hepatomegaly is caused by certain liver conditions, nausea and vomiting may occur as side effects.
Fatty liver:
- Abdominal discomfort: Discomfort or mild pain in the upper right abdominal region.
- Unexplained weight loss: Any unintended decrease in body weight.
- Weakness: Physical and emotional weakness that compromises strength levels.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of skin and eyes as a telltale sign of liver dysfunction (more prevalent among advanced cases).
- Dark urine: Urine may appear darker due to elevated bilirubin levels.
- Enlarged liver: Hepatomegaly may occur alongside fatty liver disease in certain instances.
What are the causes of Hepatomegaly and Fatty Liver
Causes of Hepatomegaly:
- infections: Hepatitis (A, B, C) and other pathogens may cause liver inflammation and enlargement.
- The Inflammatory Condition: Chronic inflammation, such as in cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) can cause Hepatomegaly.
- Metabolic Disorders: Disorders such as hemochromatosis Wilson’s disease, hemochromatosis, and glycogen storage disorders can affect normal liver function and lead to an increase in size.
- Drinking Abuse: Excessive and chronic drinking alcohol can cause an alcohol-related hepatomegaly that is characterized by liver damage and swelling.
- heart conditions: Heart failure or congestive heart conditions can result in liver congestion and hepatomegaly.
- Tumors: Malignant or benign tumors primary liver tumors and those that have metastasized can cause hepatomegaly.
Causes of Fatty Liver (NAFLD and AFLD):
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
- Obesity: Overweight and overweight are important risks for developing NAFLD.
- Insulin Resistance: The metabolic disorder and insulin resistance are related to NAFLD.
- High-Fat Diet: A diet rich in sugars and saturated fats can cause fat accumulation in the liver.
- Living a sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical exercise can worsen NAFLD.
- Genetics: Genetic factors may predispose individuals to developing NAFLD.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD):
- Extreme Alcohol Consumption: The long-term and frequent consumption of alcohol is the most common reason for AFLD.
- Quantity and Duration: Both the amount and the duration of consumption of alcohol are important in the formation of AFLD. 0000
What are the Risk Factors of Hepatomegaly and Fatty Liver?
Risk Factors of Hepatomegaly:
- Alcohol Consumption: Prolonged and excessive alcohol consumption is a major risk factor for developing hepatomegaly usually leading to alcoholic-related Hepatomegaly.
- Diseases: The risk of developing hepatomegaly increases when exposed to the Hepatitis virus (e.g. Hepatitis B as well as C) or parasites (e.g. schistosomiasis).
- Chronic Inflammation: Conditions such as autoimmune hepatitis, cirrhosis and NASH (NASH) raise the chance of developing hepatomegaly.
- Metabolic Disorders: Hemochromatosis as well as Wilson’s Disease, which results in an abnormal accumulation of metals within the body, may cause hepatomegaly.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Heart diseases, especially congestive heart failure can result in liver congestion as well as Hepatomegaly.
Risk Factors of Fatty Liver (NAFLD and AFLD):
- Obesity: Body weight excess especially abdominal obesity is a major risk cause for both non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcohol fatty liver disease (AFLD).
- Insulin Resistance: Resistance to insulin and metabolic syndrome is firmly connected to the development of NAFLD.
- High-Fat Diet: A diet that is high in sugars and saturated fats increases the risk of contracting NAFLD.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol consumption that is excessive and long-term consumption is the main risk reason for AFLD.
- A sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical exercise contributes to the growth of NAFLD.
- Genetics: Certain genetic influences could make people more prone to NAFLD as well as AFLD.
Hepatomegaly and Fatty Liver Diagnosis Method
Diagnosis of Hepatomegaly:
- Physical Exam: A healthcare provider could detect hepatomegaly on physical examinations by palpating the abdomen and observing an overly large liver.
- Testing for Imaging: Imaging techniques like ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) as well as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provide clear pictures of the liver. They help to confirm hepatomegaly and determine the severity of the condition.
- Blood tests: Blood work can detect elevated liver enzymes as well as other indicators, giving clues as to the root reason for hepatomegaly.
- A biopsy: Sometimes a liver biopsy might be required to determine the specific cause and the extent of the hepatomegaly. A small portion of the liver tissue is taken and looked at under a microscope.
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver (NAFLD and AFLD):
- Testing for Imaging: Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI are able to detect the presence of liver fat and determine its severity of. These tests are non-invasive and frequently employed methods to diagnose fatty liver.
- Testing for Blood: Blood tests can test liver enzymes and determine the liver’s function. The presence of elevated liver enzymes could be a sign of liver damage or inflammation.
- FibroScan, or Transient Elastography: This noninvasive procedure measures stiffness in the liver to determine the severity of fibrosis in the liver (scarring) which is a sign of more advanced types of fatty liver.
- Liver Biopsy: In certain instances, it is possible to have a biopsy of the liver. This can be suggested to accurately assess the state of the liver, distinguish it from NAFLD and AFLD, and to determine the severity of damage to the liver.
What are the treatments for Hepatomegaly and Fatty Liver?
Treatment for Hepatomegaly:
- The underlying cause of the problem: The primary treatment strategy for hepatomegaly involves determining and treat the root cause of the liver’s expansion. This could include managing inflammation, treating infections or managing metabolic issues.
- Medicines: In some cases, medication can be prescribed to treat symptoms or certain conditions that cause the occurrence of hepatomegaly. In particular, antiviral medicines can be prescribed for viral hepatitis. Similarly, anti-inflammatory drugs may help with the treatment of autoimmune liver disease.
- Lifestyle Changes: Changes in lifestyle, like a healthier diet or losing weight, abstaining from alcohol, and exercising regularly can be vital in preventing hepatomegaly. These changes could help to in preventing further damage to the liver and boost overall well-being.
Treatment for Fatty Liver (NAFLD and AFLD):
- lifestyle changes: Changes in lifestyle habits are crucial to managing the symptoms of fatty liver. It includes losing weight via exercising and diet and avoiding alcohol consumption and increasing the sensitivity of insulin.
- Medical Treatment: In some cases, healthcare providers can prescribe medication to treat certain aspects of the disease like insulin-sensitizing medications for NAFLD or treating issues like high cholesterol, or diabetes.
- Surgery Alternatives: Severe cases of fatty liver and its complications could necessitate surgical intervention like the transplant of a liver for patients with end-stage liver disease.
Comparison between Hepatomegaly and Fatty Liver
Here’s a comparison chart summarizing the key differences between hepatomegaly and fatty liver:
| Characteristic | Hepatomegaly | Fatty Liver (NAFLD and AFLD) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enlargement of the liver beyond its normal size | Accumulation of fat in liver cells |
| Primary Causes | Infections, Inflammatory conditions, Metabolic disorders, Alcohol abuse, Heart conditions, Tumors | Obesity, Insulin resistance, High-fat diet, Excessive alcohol consumption |
| Common Symptoms | Abdominal discomfort, Pain, Tenderness, Jaundice, Unexplained weight loss, Fatigue | Fatigue, Abdominal discomfort, Unexplained weight loss, Weakness, Jaundice (in severe cases) |
| Diagnosis Methods | Physical examination, Imaging tests (ultrasound, CT, MRI), Blood tests, Liver biopsy (if needed) | Imaging tests (ultrasound, CT, MRI), Blood tests, FibroScan, Liver biopsy (in specific cases) |
| Types (in the case of fatty liver) | N/A | Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD) |
| Lifestyle Changes | Addressing underlying cause, Medications, Healthy diet, Weight management, Alcohol abstinence, Exercise | Weight loss, Healthy diet, Sugar and fat reduction, Alcohol abstinence, Regular exercise, Blood sugar and cholesterol control |
| Treatment Options | Focused on underlying condition, Medications, Lifestyle modifications | Lifestyle changes, Medications (in some cases), Surgical options (in severe cases) |
| Prognosis | Variable depending on the cause and its severity | Good prognosis with lifestyle changes; may progress to more severe liver conditions if not managed |
| Prevention | Preventing infections, Alcohol moderation, Healthy lifestyle | Weight management, Balanced diet, Alcohol moderation, Regular exercise, Diabetes and cholesterol control |
Some lifestyle changes that can help with Hepatomegaly and Fatty Liver?
For Hepatomegaly:
- Alcohol Abstinence: In the event that alcohol consumption is the root of the problem, abstaining from alcohol is vital to recovering and preventing any further damage to the liver.
- The Healthy Diet: Choose a healthy and balanced diet that is liver-friendly. Avoid high-fat saturated oils, sweets, and processed food items. Concentrate on vegetables, fruits protein lean, and whole grains.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being able to maintain and achieve an ideal weight can ease stress in the liver, and boost its performance.
- Regular exercise: Incorporating regular physical workouts into your schedule can assist in weight reduction and general health.
- Meds Compliance: In the event that you’re prescribed medication to treat an underlying disease, you must adhere to the prescribed regimen as instructed by your physician.
For Fatty Liver (NAFLD and AFLD):
- Diet: Losing excess weight is a crucial alteration in lifestyle to improve the health of your liver. Even small weight loss can make a huge difference.
- Food Changes: Make sure you are eating a balanced, low-fat diet and cut down on sugar consumption. Include more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet.
- Reduce Alcohol Use: For people with NAFLD, it’s essential to reduce or stop drinking alcohol. In the case of AFLD total abstinence is typically required.
- Regular exercise: Engage in regular physical activity, including resistance training and aerobic exercises that aid in losing weight and boost the health of your metabolism.
- Monitor blood Sugar as well as Cholesterol: If you suffer from diabetes or high cholesterol be sure to work with your physician to manage these conditions in a timely manner, since they could affect your liver’s fatty tissue.
- Regular Check-ups: Routine medical check-ups will help you monitor your liver health and monitor the changes in your lifestyle.
Summary
Hepatomegaly, or abnormal liver enlargement due to infection, inflammation, metabolic disorders, or alcohol abuse can result in upper abdominal discomfort that is diagnosed through physical exams and imaging treatment plans that target its source.
Fatty liver, either non-alcoholic (NAFLD) or alcoholic (AFLD), refers to fat accumulation in liver cells. NAFLD is linked with obesity and insulin resistance while AFLD results from excessive alcohol consumption.
Both can progress into more serious liver conditions over time and need to be managed through lifestyle modifications, medication, and surgery as soon as possible for successful intervention. Regular medical monitoring ensures effective intervention can take place.
Focus Keyword:
Distillation, Chromatography, Separating mixtures, comparison, differences, advantages, limitations, Separation Process, Liquide and Solid Separation