Overview and key difference between Genetic and Congenital Disorders
Genetic and Congenital Disorders can have devastating repercussions for an individual’s quality of life and well-being.
These disorders may either run in families, or form spontaneously over time, and they may either be autosomal predominant, autosomal regressive, or X linked – with Down syndrome, Cystic Fibrosis, and Huntington’s Disease among them being among them.
Congenital diseases refer to conditions present at birth that impact organs, tissues, or limbs of an entire organism, including organs. Genetic or environmental influences may cause congenital diseases. Cleft lips/palettes, clubfoot conditions, and heart defects are examples of congenital disorders.
Congenital and genetic disorders differ due to their respective causes; each one may result in unique symptoms.
Healthcare providers need to understand these differences so as to provide those suffering from congenital or genetic disorders with appropriate treatments and diagnoses. Early screening, diagnosis and treatment can enable individuals with these diseases to live a fulfilling life while mitigating their negative impacts on daily activities.
Genetic Disorders
Genetic disorders are caused by genetic mutations which alter DNA sequence. They may be passed from generation to generation or can appear spontaneously at any point throughout someone’s lifespan. Such disorders include:

1. Autosomal Dominant Disorder: This form of disease results from mutations involving one gene from each pair on one autosome; they can pass down 50% of the time to children.
2. Autosomal-Recessive Disorders: Autosomal-recessive diseases result from mutations of both copies of one gene on one autosome pair; to develop one of these disorders a person must inherit both copies from both their parents.
3. X-linked diseases: These conditions result from gene mutations on the X chromosome. Though both men and women possess one copy, males seem more affected than women by such disorders since just carrying one mutated copy can make an individual susceptible whereas for females both copies must inherit mutations to experience symptoms.
Genetic disorders have various causes, from mutations occurring during cell division to heritable mutations to spontaneous ones that arise spontaneously or even randomly in individuals’ genes.
Down Syndrome, cystic fibrosis and Huntington’s disease are examples of such conditions which have varied symptoms that range in severity; while some can be managed using medication or therapy while others cannot.
Congenital Disorders
Congenital disorders, or conditions present from birth that impact various parts of the body – organs, limbs, and tissues. Congenital disorders may result from genetic or environmental causes – often manifesting organ issues as symptoms. There are various kinds of congenital disorders including:
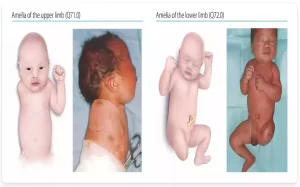
1. Structural Disorders: Structural disorders refer to any condition which alters or disrupts the structure of the body, including conditions like cleft lip and palate, clubfoot deformity or heart defects.
2. Metabolic disorders: Metabolic conditions entail disrupting how nutrients are broken down and utilized by your body, leading to the accumulation of toxins within. Phenylketonuria (PKU) and Maple Syrup Urine Disease are examples of such metabolic issues.
3. Developmental disorders: Developmental disorders refer to any condition which hinders body and brain development, leading to intellectual or developmental disabilities such as cerebral palsy or autism spectrum disorder. Examples may include cerebral palsy or autism spectrum disorder.
The causes of congenital disorders vary depending on the disorder. Genetic or environmental factors can include abnormalities in genes, maternal infections or exposure to chemicals or medications during pregnancy.
Some disorders are manageable with medication or therapy, but others may require surgical intervention or long-term management from healthcare professionals to guarantee early detection and prompt treatment. Early screening is important to identify congenital conditions and diagnose them.
Differences Between Genetic and Congenital Disorders
Genetic and congenital disorders differ considerably in numerous ways, including:
1. Definition: Genetic disorders arise when there are irregularities in an individual’s DNA while congenital disorders may or may not have genetic influences; both conditions could potentially exist at birth and could possibly contribute to additional symptoms or diseases later.
2. Causes: Genetic disorders result from mutations to DNA which may either be passed from generation to generation or occur spontaneously; congenital disorders could arise both through environmental influences as well as genes; many genetic conditions manifest physical symptoms which appear similar to congenital defects but many don’t require surgery due to environmental or gene factors alone.
3. Time of onset: Genetic Disorders Can Arise Any Time of Life, While Congenital Conditions Appear Before Birth. Congenital disorders cannot be mitigated with medication taken after birth and therefore cannot be avoided altogether.
4. Treating and Managing Genetic Disorders: Treatment options for genetic disorders depend upon their symptoms; treatments could include medication, surgery or therapy as appropriate. Unfortunately, some genetic conditions do not yet have cures while congenital disorders often necessitate multiple forms of therapy depending on severity and specifics such as surgery and medication administration.
5. Prognosis and Outcomes: Genetic and congenital disorders have highly variable prognoses and outcomes depending on their specific form, severity and when diagnosis/treatment was received. While some disorders can be managed successfully without major impact on everyday life; others could threaten an individual’s existence altogether and decrease quality-of-life significantly.
Genetic disorders arise when there are genetic mutations while congenital disorders stem from both environmental and genetic influences; healthcare providers must have knowledge about both to provide appropriate diagnosis, treatment, and management services to those afflicted.
Conclusion
Genetic and congenital conditions have the power to severely restrict an individual’s quality of life and health, often having devastating repercussions for them and their families. Congenital disorders may develop from environmental or genetic influences and vary greatly in terms of severity, treatment options and prognosis; their timeline of onset onset varies as well.
It’s imperative that healthcare providers recognize the distinctions between congenital and genetic disorders so individuals are diagnosed, managed and treated appropriately – early screening, accurate diagnosis and timely treatments help people living with these conditions lead fulfilling lives despite any restrictions caused by their conditions that limit daily activities or disrupt daily routine.