Difference Between Bed Bugs and Dust Mites
Introduction to Bed Bugs and Dust Mites
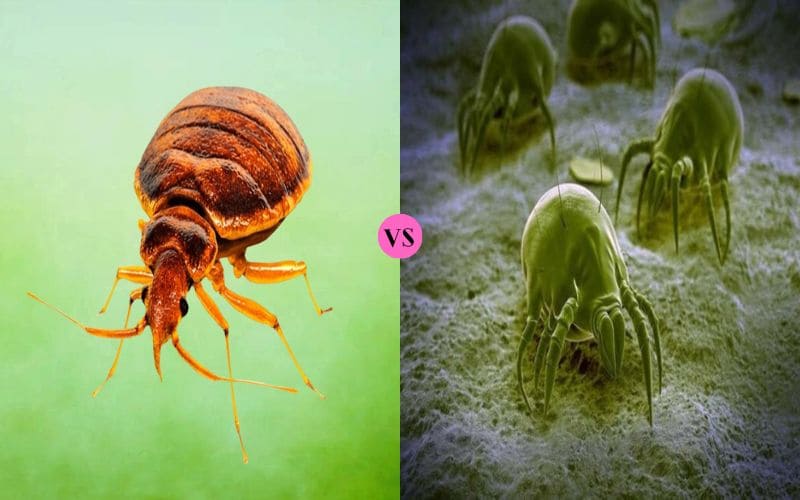
Bed Bugs and Dust Mites are contrasted in that bed bugs are arthropods that belong to the insect family, while dust mites are arthropods that are part of the Arachnidae family.
Arthropods can be described as invertebrates that have pairs of legs. They comprise 75 percent of all species living on Earth. They can be pollinators recyclers of recycled nutrients, even scavengers, and even food for other animals. Hence, they are essential for preserving ecological balance.
Arthropods are divided into four main classes myriapods, insects (centipedes millipedes, and centipedes) as well as arachnids (mites, worms, spiders including scorpions), and crustaceans (slaters or shrimps as well as crabs).
Dust mites and bed bugs are two distinct species belonging to the phylum Arthropods. Bed bugs are insects that have two antennae and three legs. Dust mites belong to the arachnid group with eight pairs of legs but no antennae.
What are Bed Bugs?

Bed bugs are small, rodents that feed on the blood of both humans and other animals. They are known to contaminate mattresses, bedding as well and furniture, to name a few. Bed bugs that are adults are usually around the size of an apple seed. They are in an oval shape.
Bed bugs are master hitchhikers. They often attach themselves to luggage, clothes, or even furniture. This makes it easy for them to travel between different locations. They are attracted by heat and carbon dioxide while they sleep. For this reason, they usually take food at night.
They can also cause red, itchy welts on the skin. Although they are not thought to carry disease, their presence can cause anxiety and sleep disturbances. Getting rid of pests is difficult and often requires the help of a professional pest control service.
To avoid bed bug infestations and bed bug infestations, you must inspect and wash bedding frequently take extra precautions when traveling, and act quickly if an infestation is suspected. Early detection and prompt intervention are essential to efficiently deal with bed bug problems.
Where can Bed Bugs live?
Bedbugs can find shelter in a variety of environments, including:
- Bedding such as mattresses, box springs, and bed frames.
- Furniture includes couches, chairs, and upholstery.
- cracked and cracked walls.
- May be hidden in the floor and furniture seams when luggage moves from the affected area to other places such as the luggage compartment.
- Electrical outlets should be exposed only when absolutely necessary, while clothing should also be used carefully.
- If infestations become severe enough, they may move into wall voids.
- Once launched they can spread to buses, trains, and planes if present in these modes of travel.
What is a Bust Mite?
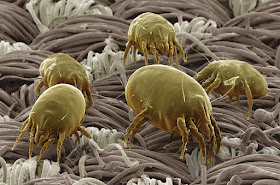
Dust mites are microorganisms found in the dust and fabric of our homes that feed on dead skin cells in humans and pets alike, often becoming a source of infection in dusty areas such as beds, carpets, upholstery, or hallways. Although almost invisible to the naked eye they measure only between 0.2-3 millimeters.
The dust itself may be harmless, their excrement and coat skin contain allergenic proteins that can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Common symptoms of dust mite allergy include sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy or watery eyes, and skin rash. When disturbed (such as when cleaning or changing bedding), their allergens become airborne and cause respiratory problems.
Regular cleaning and maintenance of the home is critical to reducing dust mite exposure, including washing bedding in hot water, using allergen-proof covers on mattresses and pillows, using regular HEPA filter vacuums, and managing humidity levels effectively as dust mites thrive under. Wet conditions as well as managing their numbers by increasing air ventilation or reducing ventilation rates.
Where can Bust Mites live?
Dust mites have the ability to live anywhere within your home and are usually found where human or pet dust or skin flakes accumulate.
Common examples are:
- Beds include mattresses, pillows and blankets
- Carpets and rugs in high-traffic areas are particularly susceptible to dust accumulation.
- upholstery such as couches, chairs, and cushions with dust-attracting fabric such as velvet; Curtains and drapes can collect even more dust.
- Curtained drapes can collect debris such as toys that are not regularly cleaned on their owners.
- Stuffed toys require regular attention if not soiled.
- Clothing that collects dust may also need attention; HVAC systems can become dusty as pet bedding accumulates dust in pet sleeping areas and air ducts.
- Car carpet if unchanged. They can deteriorate rapidly over time.
Early symptoms of Bed Bugs and Dust Mites
Early symptoms of bed bugs:
- Bites: small itchy red rashes on the skin that may cluster together or line linearly on exposed body parts such as hands and feet; Crushing can also result in blood stains from bed bug infestations on sheets, pillowcases, or clothing, such as blood-red stains under pillows and clothing from crushed bed bugs.
- Dark stains: Small dark stool stains on bedding, mattresses, or surrounding furniture can indicate bed bug activity.
- Musty Odor: Heavy bedbug infestations often emit an unhealthy, musty odor that often lasts for months after their presence is eradicated.
- Visible Bugs: Sometimes adult bed bugs can be seen shedding skin around your bed as well; Also early symptoms of dust mites may include patches that appear around the mattress where the dust mites have settled.
Early Signs of Dust Mites:
- Allergic reactions: Early symptoms may include allergic symptoms such as sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy or watery eyes and skin rash – especially after waking up or resting in bed.
- Visible Dust: The presence of dust mites is often identified by visible dust particles where dead skin cells are deposited.
- Coughing and wheezing: Some people may experience coughing or wheezing in response to dust mite allergens present.
- Scratching at night: If you are sensitive to dust mite allergens found in bedding, scratching can become an uncomfortable nighttime habit when exposed.
Causes of Bed Bugs and Bust Mites
Bed Bugs and dust mite infestations have several causes.
Here are the primary factors that contribute to their presence:
Bed Bugs:
- Travel and Infested Items: Bed bugs can infest luggage, clothes, and furniture while traveling or buying secondhand items; Then spread to new places.
- Avoid human contact: Bed bugs are usually spread by human interaction and can be transferred between infested locations through visits by friends and family members.
- High Traffic Areas: Hotel rooms, dormitory halls, and apartment buildings that experience frequent turnover enable them to spread quickly as they move between units more freely than ever before.
- Clutter: Cluttered living spaces provide more hiding places for bed bugs, making infestations harder to detect.
- Lack of awareness: Poor knowledge about bed bugs and their hiding methods can hinder detection and treatment efforts, resulting in delays.
Dust Mites:
- Human and pet dander: Dust mites feed on dead skin cells shed by humans and animals alike, inviting areas with abundant dander to collect dust and nest.
- Moisture: Dust mites thrive in moist environments. High indoor humidity levels create ideal conditions for their proliferation.
- Lack of ventilation: Lack of proper ventilation or airflow can increase humidity levels and contribute to dust mite infestations, further contributing to moisture-induced dust mite infestations and dust mite infestations.
- Neglected cleaning: Infrequent dusting and vacuuming can increase the number of dust mites that will find a food source in dust deposits – such as dead skin cells. This, in turn, feeds their growth.
- Old bedding and upholstery: Old mattresses, pillows, and upholstery harbor more dust mites due to the build-up of skin cells over time.
How do they spread
Bed Bugs:
- Bed Bugs in Travel: Travel is often an opportunity for bed bugs to travel unknowingly from infested locations into new ones and spread. Bedbugs attach themselves unwittingly when people transport luggage from an infestation site into an unknown one and continue moving between different environments with them unknowingly spread throughout.
- Visitors: Bed bug infestation can easily happen when guests bring them in on their belongings; bed bugs have the ability to hide within clothing, bedspreads and mattresses they carry around with them.
- Shared Items: Borrowing or purchasing used furniture without conducting thorough checks can introduce bed bugs into new environments, increasing the risk of infestation.
- Movement Within Buildings: Bed bugs have the ability to easily spread in multi-unit housing or hotels by moving between adjacent units through wall voids, electrical outlets, and plumbing pipes.
Dust Mites|:
- Everywhere: Indoor environments often experience an infestation of dust mites that thrive under warm and humid conditions and feed off dead skin cells shed by people and pets alike. They feed off of dead cells left over from these sources of skin that have yet to shed off, feeding on an endless source of dead skin cells from humans and pets alike.
- Dust and Airborne Particles: Dust mite waste products make up part of household dust; when this dust is disturbed, its particles become airborne and may be breathed in by inhalers.
- Bedding and Upholstery: Dust mites thrive in environments where dead skin cells accumulate, such as bedding, pillows, mattresses, upholstered furniture or carpeting. They tend to thrive especially well.
Difference Between Bed Bugs and Dust Mites
The arthropods are bed bugs, which are part of the insect family, and dust mites, on the other hand, are arthropods that belong to the arachnid species. That’s the main difference between dust mites and bed bugs. Bed bugs measure 0.19 or 0.28 inches long while dust mites range from 0.004 up to 0.157 inches.
Here’s a comparison chart highlighting the key differences between bed bugs and dust mites:
| Characteristic | Bed Bugs | Dust Mites |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Larger, around the size of an apple seed | Microscopic, about 0.2-0.3 mm in size |
| Color | Reddish-brown | Transparent, often not visible |
| Shape | Flat and oval-shaped | Tiny, oval-shaped |
| Feeding Behavior | Blood-feeding, typically at night | Feed on dead skin cells and organic matter, mostly in dust |
| Nocturnal | Yes | Yes |
| Hiding Places | Bed frames, mattresses, furniture | Bedding, carpets, upholstery, and dust |
| Health Implications | Bites may cause skin reactions | Allergenic proteins in feces and shed skin can trigger allergies |
| Disease Transmission | Not known to transmit diseases | Not known to transmit diseases |
| Detection | Visible to the naked eye | Microscopic and often not visible |
| Prevention and Control | Requires professional pest control | Regular cleaning, allergen-proof covers, and humidity control |
| Common Health Issues | Skin irritation, psychological stress | Allergic reactions (sneezing, runny nose, skin rashes) |
| Size | Larger, around the size of an apple seed | Microscopic, about 0.2-0.3 mm in size |
| Color | Reddish-brown | Transparent, often not visible |
| Shape | Flat and oval-shaped | Tiny, oval-shaped |
| Feeding Behavior | Blood-feeding, typically at night | Feed on dead skin cells and organic matter, mostly in dust |
| Nocturnal | Yes | Yes |
| Hiding Places | Bed frames, mattresses, furniture | Bedding, carpets, upholstery, and dust |
| Health Implications | Bites may cause skin reactions | Allergenic proteins in feces and shed skin can trigger allergies |
| Disease Transmission | Not known to transmit diseases | Not known to transmit diseases |
| Detection | Visible to the naked eye | Microscopic and often not visible |
| Prevention and Control | Requires professional pest control | Regular cleaning, allergen-proof covers, and humidity control |
| Common Health Issues | Skin irritation, psychological stress | Allergic reactions (sneezing, runny nose, skin rashes) |
Treatment options and strategies for getting rid of bed bugs and dust mites?
Effective strategies and treatment solutions for eliminating bed bugs and dust mites include:
Bed Bugs:
- Professional Extermination: For effective bed bug eradication, hiring a licensed pest control service professional is often the most efficient approach. Their combination of insecticides, heat treatments, and other tactics may prove more successful in eliminating bed bugs than trying to do it alone.
- Heat Treatments: An effective method for eliminating bed bug populations in infested environments involves raising temperatures to levels that kill bed bugs and their eggs; this process requires special tools.
- Steam Cleaning: Steam can quickly eliminate bedbugs and their eggs on contact, making this technique ideal for treating mattresses and upholstery.
- Mattress and Furniture Encasements: Special covers designed to trap bed bugs can protect mattresses and box springs against their escape or from biting; thus preventing bed bug populations from growing out of control and spreading further.
- Vacuuming: Vacuuming infested areas regularly and disposing of the vacuum bag can help decrease their population.
- Dismantle and Clean: Breaking apart bed frames and cleaning all parts thoroughly can eliminate potential sources of trouble spots in a bed frame.
Dust Mites:
- Allergen-Proof Covers: Cover Your Mattress, Pillow, and Duvet With an Antiallergen Material To Help Prevent Allergies Anti-allergen covers can protect mattresses, pillows, and duvets against dust mites that come into direct contact with skin to cause allergies. By covering them up you prevent dust mites from making contact and leading to further allergy attacks.
- Frequent Washings: Regularly washing bedding, curtains, and toys in hot water (at least 130 degrees or 54 degrees) will kill dust mites that thrive within them.
- Dehumidification: Maintain indoor humidity levels under 50% to reduce dust mite populations that thrive in high moisture environments, as they thrive there.
- HEPA Filtration: HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters should be installed in vacuum cleaners and air purifiers in order to trap dust mite particles and keep air from becoming polluted with pollutants such as pollen or dirt mites.
- Regular Cleaning and Dusting: Set a reminder in your calendar every six weeks or so to clean and dust the areas in your home that collect dust. Pay particular attention to those areas where dust tends to build up.
- Freezing: For items such as stuffed toys that cannot be washed (e.g., pillows and throw blankets), placing them in the freezer to kill dust mites may be an effective way of providing an antimicrobial defense system against dust mite infestation.
- Chemical Treatment: When all else fails, chemical acaricides (drugs designed to kill mites) may be employed, such actions should only ever be seen as the last resort.
What are the health risks of Bed Bugs and Dust Mites?
Health Risks Associated with Bed Bugs:
- Skin Irritation: Bed bug bites may cause itching, redness, and discomfort that leads to scratching causing secondary skin infections and potentially lead to secondary problems with secondary bite infections.
- Allergic Reactions to Bed Bug Bites: Bed bug bites may trigger allergic reactions in some individuals ranging from mild to severe reactions.
- Psychological Distress: Chronic bed bug infestations may create anxiety, stress, and sleep disruption due to fear of being Bit: this fear often prompts many victims of persistent bedbug infestations to resort to medical interventions in an effort to control an infestation and possibly relieve anxiety symptoms.
- Scratching Bed Bug Bites Can Increase the Risk of Secondary Infections: Scratching bed bug bites may damage skin cells and increase your risk for secondary bacterial infections, making scratching bites even more likely to happen.
- Anemia (Rare): When infestations become particularly serious – particularly among vulnerable populations such as infants or the elderly – blood loss from multiple bites may lead to anemia, leading to severe health consequences and impairment.
Health Risks Associated with Dust Mites:
- Allergic Reactions: Dust mite allergens found primarily in their feces and shed skin can trigger allergic reactions that include symptoms like sneezing, runny/stuffy noses, itchy/watery eyes, coughing fits, and skin rashes.
- Asthma Exacerbation: Dust mite allergens have long been identified as one of the primary triggers of asthma attacks and are frequently responsible for worsening respiratory symptoms in those living with asthma.
- Eczema Aggravation: Dust mite allergens have the power to worsen eczema (atopic dermatitis) symptoms for those sensitive to them, leading to itchy and inflamed skin conditions that flare up on exposed parts of their bodies.
- Difficulties Breathing: Individuals suffering from severe dust mite allergies may have difficulty breathing at night. This often manifests itself with difficulty swallowing.
- Sleep Disturbances: Allergic reactions to dust mites may interfere with our natural sleeping cycles and cause daytime fatigue as well as decrease quality of life.
Tips for Avoiding Bed Bugs and Dust Mites in Your Home
Bed Bugs:
- Inspect Used Items: Before purchasing used furniture or clothing that could contain bed bugs for yourself or bringing into the home used items must first be thoroughly examined for signs of bed bug activity before being brought indoors.
- Be Careful When Traveling: Be on guard against bedbugs by inspecting hotel rooms thoroughly before placing luggage on the floor; once back home, wash and dry any clothing worn while traveling in high heat before folding it away in storage.
- Declutter: Reduce clutter to lower bed bug numbers in your home and cut down on hiding places for these pests.
- Encase Mattresses and Box Springs to Prevent Bed Bug Infestations: Invest in bed bug-proof covers to safeguard mattresses and box springs against potential infestation.
- Regular Vacuuming: Vacuum carpets, rugs, and upholstery regularly and discard your vacuum bag outdoors.
- Seal Cracks and Crevices: Seal any crevices in walls, furniture, or baseboards where bed bugs might hide out in order to eliminate potential bed bug shelter sites.
- Care Should Be Exercised with Secondhand Items: Exercise caution when purchasing second-hand furniture and clothing items. Thoroughly inspect and clean them prior to bringing them into your home.
Dust Mites:
- Use Allergen-Proof Covers: For maximum dust mite control, place mattresses, pillows, and duvets inside allergy-proof covers to protect them from dust mite infestation. Dust mites have no way into these areas where allergen-proof covers exist!
- Wash Bedding Regularly: Regularly wash bedding (sheets, pillowcases, and blankets) in hot water of at least 130F or 54C to extend its longevity and avoid staining and wear and tear.
- Reduce Humidity: Dehumidifiers can help keep indoor humidity below 50% in bedrooms, especially.
- Use of HEPA Filtration Device: Use a vacuum with a HEPA filter regularly to clean carpets, rugs, and upholstery to help preserve its lifespan and ensure good indoor air quality.
- Consider hard flooring surfaces instead: For better airflow and a healthier indoor environment, invest in hard flooring like carpet or tile instead of carpet, which trap dust particles.
- Reduce stuffed toys in the bedroom: Where possible, minimize the number of stuffed toys in the bedroom or wash them regularly in hot water.
- Freeze Stuffed Items: When regularly washing stuffed items is not possible, refrigerate for at least 24 hours to kill dust and reduce allergen levels. This should do just the trick!
- Regular cleaning: Regular dusting and cleaning of areas where dust accumulates. Pay particular attention to areas prone to generating dust particles.
Summary
Bed bugs are small reddish-brown insects that feed on human blood and infest bedding and furniture, often leaving bite marks that cause skin irritation despite not transmitting disease. When an infestation occurs, professional pest control treatment is needed as soon as possible to eliminate the infestation.
Dust mites, on the other hand, are small arachnids that feed on dead skin cells found in dust and grow within. Although barely detectable with the naked eye, dust particles have the ability to cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals; Regular cleaning, allergen-proof covers, and humidity control all help effectively control dust mite populations.
Both bed bugs and dust mites are threats to households, bed bugs cause skin problems while dust mites often trigger allergies, with different methods for prevention and control for each insect species.

