Atropine and Epinephrine are two essential medications that have been widely used for their distinct properties and life-saving abilities. This article will delve into the applications, mechanisms, and characteristics of various drugs to shed light on their impacts across different medical scenarios.
What is Atropine?
Atropine is a medication derived from the deadly nightshade plant (Atropa belladonna) and certain other related plants. Anticholinergic medicines work by blocking acetylcholine. Acetylcholine transmits nerve signals to the parasympathetic system of the autonomic nervous system which regulates all nonvoluntary bodily processes.
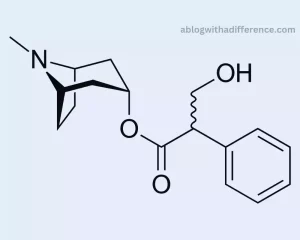
Atropine works to block the effects of Acetylcholine and has various physiological impacts including:
1. Increased Heart Rate: Atropine produces a faster heartbeat by diminishing the effect of parasympathetic stimulation on heart muscle contraction.
2. Dilation of the Pupils: Mydriasis refers to an eye condition caused by Atropine that leads to dilation or dilatation of its pupil, distorting vision. This effect is utilized in ophthalmology for eye examinations and certain surgical procedures.
3. Reduced Salivation and Respiratory Secretions: Atropine can decrease the production of saliva and respiratory secretions, making it useful in anesthesia and certain medical conditions.
4. Relaxation of Smooth Muscles: It can lead to the relaxation of smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract and urinary bladder, which may be beneficial in certain medical situations.
Due to these pharmacological effects, Atropine finds applications in various medical fields, including ophthalmology, cardiology, and anesthesia. For example, it is used to dilate pupils during eye exams, increase heart rate in cases of bradycardia (abnormally slow heart rate), and reduce excessive salivation and respiratory secretions during surgery.
Atropine can have side effects and contraindications; therefore it should only be prescribed after carefully considering both medical conditions as well as any additional factors pertaining to each individual patient. To ensure safe and effective Atropine usage, it is crucial that patients adhere to the guidance and advice from qualified healthcare providers.
What is Epinephrine?
Tyrosine, an amino acid derivative belonging to the catecholamine group of compounds. Epinephrine plays an essential role in activating your “fight or flight” response a physiological mechanism designed to allow for quick responses in times of danger or distress. With it comes increased alertness so you can respond more swiftly in situations that demand it.
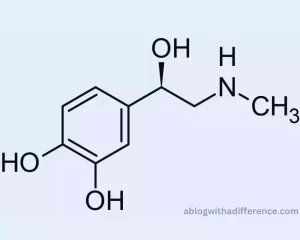
As part of its natural defense mechanism, the sympathetic nervous system activates in response to threats or stressful circumstances in our environment. Subsequently, physiological responses occur within the body in response to perceived threats.
1. Increased Heart Rate: Epinephrine stimulates the heart, leading to an increase in heart rate (positive chronotropic effect) and increased cardiac output.
2. Bronchodilation: It relaxes the smooth muscles surrounding the bronchioles in the lungs, leading to improved airflow and increased oxygen intake.
3. Vasoconstriction: Epinephrine reduces blood vessel diameter in various organ systems such as digestive and skin systems, raising blood pressure while redirecting it toward the brain and muscles.
4. Glycogenolysis: The breakdown of glycogen stores in muscles and the liver provides an immediate energy source that meets the body’s increased requirements for energy. Epinephrine, produced naturally within our bodies, can serve as an indispensable medication in medical emergencies.
Epinephrine comes in several different forms, such as auto-injectors, injectable solutions, and auto-injectors.
When used for emergency medicine purposes, Epinephrine primarily comes into play during two instances: (1) cardiac arrests and (2) hypoxia situations.
1. Anaphylaxis: Epipen is often prescribed for severe allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis. These treatments may relieve symptoms such as airway constriction and hives. Low blood pressure is another potentially life-threatening complication during an allergic response.
2. Cardiac Arrest: In advanced life support protocols during cardiac arrest situations, Epinephrine is administered to help restart the heart and maintain circulation. Due to its potency and the potential for significant effects, the administration of Epinephrine requires proper training and adherence to dosing guidelines.
It is essential to seek immediate medical attention after administering Epinephrine, even if the symptoms improve, as further evaluation and treatment are necessary in emergency situations.
Importance of understanding the differences between Atropine and Epinephrine drugs
Understanding the differences between Atropine and Epinephrine is of utmost importance for several reasons, both from a medical and patient safety perspective:
1. Appropriate Medication Selection: Atropine and Epinephrine have different mechanisms of action and target different physiological systems. Knowing these differences helps healthcare professionals choose the right medication for a specific medical condition. Administering the wrong drug could lead to ineffective treatment or even exacerbate the patient’s condition.
2. Safety and Adverse Effects: Both drugs may produce side effects which are potentially dangerous and affective. Understanding their unique profiles helps healthcare providers anticipate and manage possible complications, ensuring patient safety and minimizing the risk of adverse outcomes.
3. Specific Indications: Atropine and Epinephrine are used in distinct medical scenarios. Knowing when and how to use each drug appropriately ensures they are used only when necessary, avoiding unnecessary exposure and reducing the risk of inappropriate drug use.
4. Emergency Response: Epinephrine is an invaluable emergency medication, used to treat anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest and other urgent situations. Understanding the correct indications for each drug helps healthcare providers respond promptly in emergencies, potentially saving lives.
5. Treatment Efficacy: Understanding the effects and mechanisms of Atropine and Epinephrine will enable healthcare providers to provide patients with optimal treatment outcomes, leading to positive treatment outcomes.
6. Avoiding Drug Interactions: Understanding the differences between these medications is vital in order to avoid potential interactions when combined with other medicines. Some drug combinations can be harmful or render the medications less effective.
7. Patient Education: Education of patients about their medication will assist them in sticking with their treatment plans and understanding any possible adverse side effects or inappropriate usage of prescribed drugs.
8. Special Patient Populations:Atropine or Epinephrine can be administered differently for various patient populations, including children, pregnant people or the elderly. Understanding these differences is crucial for providing personalized and safe care.
9. Avoiding Medication Errors: Healthcare professionals need to be vigilant to prevent medication errors. Having a clear understanding of the distinctions between Atropine and Epinephrine reduces the likelihood of prescribing, dispensing, or administering the wrong drug.
10. Research and Development: Understanding the unique properties and mechanisms of these drugs aids researchers and pharmaceutical companies in developing new medications and improving existing treatments.
Understanding the difference between Atropine (Atropine) and Epinephrine (Epinephrine) can assist healthcare providers with making more informed decisions and protecting patient safety, and in providing treatment that addresses specific patient medical needs.It contributes to better emergency responses, reduces medication errors, and supports ongoing medical research and development.
Difference Between Atropine and Epinephrine
Pharmacological Background
The pharmacological background of Atropine and Epinephrine involves understanding their respective classifications.
Mechanisms of action, and effects on the nervous system:
Atropine:
1. Classification: Atropine is classified as an anticholinergic drug or an antimuscarinic agent. It falls under the broader category of parasympatholytic drugs.
2. Mechanism of Action: Atropine and acetylcholine compete to bind to muscarinic nerve receptors within networks of cholinergic neurons, inhibiting their activity. By doing so, Atropine acts as a competitive antagonist, preventing acetylcholine from binding and exerting its effects.
3. Effects on the Autonomic Nervous System: Atropine is often prescribed to minimize parasympathetic system activity and enhance sympathetic output, creating a dominant sympathetic effect. The autonomic system regulates various involuntary bodily processes. By blocking the parasympathetic activity, Atropine induces the following effects: Increased heart rate (positive chronotropic effect)
- Dilated pupils (mydriasis)
- Decreased salivation and respiratory secretions
- Relaxation of smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract and urinary bladder
- Inhibition of gastrointestinal motility and secretions
Epinephrine:
1. Classification: Epinephrine is a catecholamine and falls under the broader category of sympathomimetic drugs or adrenergic agonists.
2. Mechanism of Action: It can bind to both alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors. The specific effects depend on the receptor subtype and the tissue or organ on which it acts. Responding to danger or stress, adrenal glands release the endogenous hormonal hormone epinephrine as an endogenous hormonal signal.
3. Effects on the Sympathetic Nervous System: Epinephrine stimulates the sympathetic nervous system and triggers its “fight or flight” response. Its effects include: Increased heart rate and force of contraction (positive inotropic and chronotropic effects)
- Dilation of the bronchioles (bronchodilation)
- Vasoconstriction in certain vascular beds, raising blood pressure
- Promotion of glycogenolysis in the liver and muscles, leading to an increase in blood glucose levels
- Increased metabolic rate and energy expenditure
Atropine is an anticholinergic drug that inhibits the parasympathetic nervous system, while Epinephrine is a sympathomimetic drug that activates the sympathetic nervous system. Their distinct mechanisms of action result in different physiological effects, making them valuable medications for various medical conditions. Understanding these pharmacological backgrounds is crucial for appropriate drug use and patient safety.
Medical Uses
Medical Uses of Atropine:
1. Ophthalmology: Atropine is commonly used in ophthalmology to dilate the pupil (mydriasis). This is beneficial for eye exams, retinal examinations, and certain surgical procedures.
2. Cardiology: Atropine is used in cardiology to treat bradycardia (abnormally slow heart rate) and certain heart rhythm disorders. It can increase heart rate by blocking the parasympathetic tone on the heart’s natural pacemaker, the sinoatrial (SA) node.
3. Anesthesia: During surgery, especially those involving the airways, Atropine can be administered to reduce excessive salivation and respiratory secretions. This helps maintain a clear airway and prevent complications during anesthesia.
Medical Uses of Epinephrine:
1. Anaphylaxis: Epinephrine is the first-line treatment for severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis. Airway constriction and hives may also be relieved through breathing exercises, while low blood pressure poses serious danger during an allergic response.
2. Cardiac Arrest: Epinephrine is a critical component of advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) protocols for the management of cardiac arrest. It is administered to help restart the heart and maintain circulation during resuscitation efforts.
3. Asthma: Epinephrine can help relieve breathing difficulty during severe asthma attacks.
Qualified healthcare professionals should decide the appropriateness of administering these drugs based on an individual patient’s unique requirements and medical condition. Proper dosage, administration, and monitoring are essential for safe and effective use in the indicated situations.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage and Administration of Atropine:
The dosage and administration of Atropine vary depending on the specific medical condition being treated and the formulation used (injectable, oral, or ophthalmic). Always follow the prescribing healthcare professional’s instructions or the hospital’s protocol. The information provided below is general and may not apply to all situations:
1. Bradycardia and Heart Rhythm Disorders: In adults, the typical intravenous (IV) dose for bradycardia is 0.5 to 1 milligram (mg) every 3 to 5 minutes, up to a maximum total dose of 3 mg. For certain heart rhythm disorders, the dose may be adjusted based on the patient’s response.
2. Anesthesia: The dosage for anesthesia-induced excessive salivation and respiratory secretions may range from 0.4 to 0.6 mg IV.
3. Ophthalmology: For pupil dilation during eye exams or surgery, Atropine eye drops are used. The usual dose is one to two drops of 1% solution in the affected eye(s).
Please note that dosages may differ for pediatric patients or patients with specific medical conditions. Always consult a healthcare professional for the appropriate dosage and administration specific to the individual patient.
Dosage and Administration of Epinephrine:
The dosage and administration of Epinephrine also vary based on the specific indication and the formulation used (injectable or auto-injector). Again, follow the prescribing healthcare professional’s instructions or the emergency medical protocol. Here are some general guidelines:
1. Anaphylaxis: For the treatment of anaphylaxis, the standard dose of Epinephrine is 0.3 mg injected intramuscularly (IM) into the outer thigh. This can be repeated every 5 to 15 minutes if necessary, and a lower dose (0.15 mg) is recommended for pediatric patients.
2. Cardiac Arrest: During advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) in cardiac arrest situations, Epinephrine is administered intravenously (IV) or intraosseously (IO). A common dose recommendation is 1 mg every three to ten minutes.
3. Asthma: Sometimes a subcutaneous or intramuscular injection of 0.3-0.5mg may be required.
Epinephrine Auto-Injectors are pre-filled and designed for self administration.Education about auto-injector use and administration as well as when to seek medical help after use is of vital importance for patient success.
As with Atropine, dosages may differ for pediatric patients and those with specific medical conditions. Always seek guidance from a healthcare professional for accurate dosing and administration instructions for each individual patient’s needs.
Adverse Effects and Contraindications
Adverse Effects of Atropine:
While Atropine can be beneficial in certain medical situations, it may also lead to various adverse effects, particularly due to its anticholinergic properties.
Common side effects may include:
1. Dry Mouth: Atropine reduces salivation, leading to dryness in the mouth.
2. Blurred Vision: Pupil dilation caused by Atropine may result in temporary blurred vision and sensitivity to light.
3. Increased Heart Rate: Atropine’s action on the heart can lead to tachycardia (rapid heart rate).
4. Urinary Retention: It can cause difficulty in emptying the bladder, particularly in males with prostate enlargement.
5. Constipation: Atropine can slow down gastrointestinal motility, leading to constipation.
6. Confusion and Memory Impairment: Some individuals particularly seniors, may experience confusion or memory impairment after taking Atropine.
7. Dry Skin and Flushing: Reduced sweating due to Atropine can lead to dry skin and occasional flushing.
8. Increased Intraocular Pressure: Some patients taking Atropine may experience worsened symptoms of their glaucoma after beginning therapy with it.
Contraindications of Atropine:
Atropine is contraindicated in certain situations due to its potential risks and effects.
Contraindications include:
1. Glaucoma: Atropine can exacerbate narrow-angle glaucoma by increasing intraocular pressure, which can lead to a sudden and severe eye condition.
2. Urinary Retention: Atropine may worsen urinary retention in individuals with prostatic hypertrophy (enlarged prostate) or urinary obstruction.
3. Severe Ulcerative Colitis: Atropine may lead to toxic megacolon in patients suffering from severe ulcerative bowel disease and pose a life-threatening threat.
4. Myasthenia Gravis: Atropine may exacerbate muscle weakness among individuals suffering from myasthenia gravis, a neurological disease.
5. Hypersensitivity: People allergic or sensitive to Atropine should avoid using it.
Adverse Effects of Epinephrine:
Epinephrine is a potent medication, and while it is life-saving in emergencies, it can also lead to adverse effects, especially when administered in excessive doses. Common side effects may include:
1. Increased Heart Rate: Epinephrine can cause tachycardia and palpitations.
2. Elevated Blood Pressure: Increased blood tension may result from such actions.
3. Headache: Some individuals may experience headaches after receiving Epinephrine.
4. Tremors and Nervousness: Epinephrine may induce tremors and feelings of nervousness or anxiety.
5. Nausea and Vomiting: Epinephrine can cause gastrointestinal disturbances.
Contraindications of Epinephrine:
Epinephrine has certain contraindications due to its potential adverse effects and interactions.
Contraindications include:
1. Hypersensitivity: Individuals with known hypersensitivity or allergy to Epinephrine or its components should not receive the medication.
2. Certain Heart Conditions: Under certain cardiac conditions, such as ventricular fibrillation and tachycardia epinephrine must be avoided to ensure safe heart Functioning.
3. Narrow-Angle Glaucoma: Epinephrine can exacerbate narrow-angle glaucoma, similar to Atropine.
4. Hypertension: Uncontrolled hypertension patients should use Epinephrine with care and only in moderation.
5. MAO Inhibitors: Epinephrine can interact with monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, leading to severe hypertension.
6. Certain Anesthetic Agents: Epinephrine should be used cautiously with certain anesthetics due to potential interactions.
Conforming with proper dosing instructions in order to minimize potential side effects.
Drug Interactions

Atropine and Epinephrine may interact with certain drugs, substances, and medical conditions causing undesirable side effects or reduced effectiveness. This interaction could potentially produce unexpected reactions or reduced efficacy.
Here are some important drug interactions for each:
Drug Interactions with Atropine:
1. Anticholinergic Agents: Concurrent use of multiple anticholinergic drugs with Atropine can potentiate anticholinergic effects and increase the risk of side effects such as dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, and urinary retention.
2. Antihistamines: Combine Atropine with antihistamines for enhanced anticholinergic action that may worsen symptoms.
3. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): MAOIs can enhance the anticholinergic effects of Atropine, leading to a higher risk of side effects.
4. Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs): TCAs can also potentiate the anticholinergic effects of Atropine, increasing the risk of side effects.
5. Digoxin: Atropine increases heart rate by stimulating electrical impulses within the heart, potentially exacerbating arrhythmias when used together with Digoxin.
6. Propranolol: Propranolol and other beta-blockers can lead to sudden increases in both your blood pressure and heart rate. Atropine or beta-blockers could potentially trigger such effects and thus bring on unexpected increases in both.
7. Antidiarrheal Medications: Atropine can reduce gastrointestinal motility. Constipation may worsen with antidiarrheal medication taken concurrently.
8. Antipsychotic Medications: Combinations of Atropine with certain antipsychotic drugs may increase the risk for heat-related adverse effects due to reduced sweating.
Drug Interactions with Epinephrine:
1. Beta-Blockers: Beta-blockers can inhibit the effects of Epinephrine, leading to reduced heart rate and blood pressure response during emergencies. These interactions may prove life-threatening if anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest or other severe health conditions strike.
2. Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs): TCAs can potentiate the cardiovascular effects of Epinephrine, leading to an increased risk of arrhythmias and hypertension.
3. Alpha-Blockers: Concurrent use of Epinephrine with alpha-blockers can lead to a diminished vasoconstrictive effect and potentially worsen hypotension.
4. General Anesthetics: Epinephrine can have serious cardiovascular ramifications when taken alongside certain anesthetic agents.
5. MAO Inhibitors: MAOIs can prolong the effects of Epinephrine, leading to increased cardiovascular effects and potential hypertensive crises.
6. Digoxin: Epinephrine can decrease Digoxin levels in the blood, possibly reducing its efficacy.
7. Other Sympathomimetic Drugs: Combining sympathomimetic medications could increase their effects and increase risk for adverse cardiovascular reactions.
It is vital for healthcare professionals to review a patient’s medication list thoroughly before administering Atropine or Epinephrine to avoid potential interactions. Before beginning treatment for any condition or medication, patients must inform their healthcare providers of all relevant details about themselves such as medications taken currently or previously and any conditions which they are currently or previously experiencing.
Emergency Situations and First Aid
Atropine in Emergency Situations and First Aid:
1. Nerve Agent Poisoning: Atropine is a critical component of the treatment for nerve agent poisoning. Drug is designed to counteract excessive effects of Acetylcholine which are released as a response to nerve agents. The specific dosing and administration depend on the severity of the poisoning and the medical guidelines in place.
2. Bradycardia and Heart Block: In emergency situations where a patient presents with severe bradycardia (very slow heart rate) or certain heart blocks, Atropine can be used to increase the heart rate and improve cardiac output.
3. Organophosphate Poisoning: In cases of organophosphate poisoning (e.g., insecticides), Atropine may be given to counteract the toxic effects and restore proper organ function.
First Aid for Atropine Use:
In most emergency situations involving Atropine, the administration is performed by healthcare professionals, such as emergency medical responders, paramedics, or physicians.
In some settings where first aid may be required, such as nerve agent exposure in military or chemical accident scenarios, trained personnel may administer Atropine auto-injectors. Emergency situations necessitate that individuals receive proper training on how to utilize Atropine Auto-Injectors.
Epinephrine in Emergency Situations and First Aid:
1. Anaphylaxis: Epinephrine is the first-line treatment for anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction that can be life-threatening. It is administered as an immediate intervention to reverse symptoms like airway constriction, low blood pressure, and hives.
2. Cardiac Arrest: During cardiac arrest, Epinephrine is a crucial medication used in advanced life support protocols. It is administered intravenously (IV) or intraosseously (IO) to help restart the heart and maintain circulation.
First Aid for Epinephrine Use:
Epinephrine is often administered using auto-injectors, such as EpiPen or similar devices. These auto-injectors were specially developed for use during anaphylaxis emergencies.
If you or someone else is experiencing a severe allergic reaction with symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling, hives, or low blood pressure, and you have been prescribed an Epinephrine auto-injector, follow these steps:
1. Remove the safety cap from the auto-injector.
2. Hold the auto-injector firmly in your dominant hand with the needle end pointing down.
3. Place the needle end against the outer thigh, midway between the hip and knee.
4. Press the auto-injector firmly against the thigh until you hear or feel a click, which indicates the injection has started.
5. Holding the auto-injector for several moments will ensure that a full dose is given.
6. Seek immediate medical attention after administering Epinephrine, even if the symptoms improve.
It is crucial to seek medical help promptly after administering Epinephrine, as a severe allergic reaction requires comprehensive medical evaluation and further treatment.
Remember that these emergency situations can be life-threatening, and it is essential to contact emergency medical services (EMS) immediately for professional medical care and further treatment.
Conclusion
Atropine and Epinephrine have transformed emergency situations and life-threatening illnesses. Healthcare professionals and the general public alike must become acquainted with their mechanisms of action, medical uses and precautions, side effects as well as potential improvements as medical research progresses. We can expect to witness further advancements as medical research progresses.