Immunoprecipitation and Coimmunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation is a widely utilized laboratory technique used to isolate and purify specific proteins from complex protein mixtures. The method relies on interactions between antibodies and antigen, which capture target proteins within these complex mixtures of proteins.
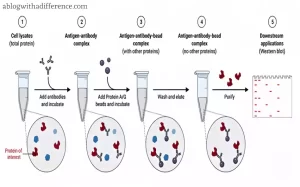
Other applications for immunoprecipitation include quantifying proteins, detecting protein interactions between two or more proteins and isolating posttranslational modifications – making this an incredibly powerful way of studying their function and interactions; in turn it has expanded our knowledge about cell signaling, disease mechanisms as well.
Coimmunoprecipitation is an advanced version of Immunoprecipitation used to isolate and purify bound protein complexes in vivo. Co-IP utilizes two antibodies instead of just one antibody to capture complexes; therefore providing greater potential in studying interactions among proteins as well as discovering novel complexes; it allows isolation of complexes not stable in vitro as well as providing insight into individual protein roles within complex cell processes.
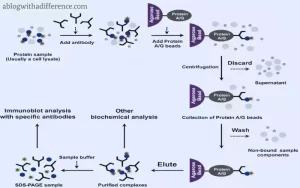
Differences between Immunoprecipitation and Coimmunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation refers to a technique that precipitates proteins out of solution with antibodies using specific techniques, Coimmunoprecipitation precipitates intact protein complexes with antibodies as opposed to proteins themselves. this difference marks immunoprecipitation’s primary distinction from coimmunoprecipitation. immunoprecipitation is more frequently employed within laboratories while coimmunoprecipitation remains less frequently utilized by scientists.
This infographic presents immunoprecipitation and coimmunoprecipitation differences as tabular comparisons for ease of reference.
Immunoprecipitation and coimmunoprecipitation are two precipitation reaction-based techniques involving antigen-antibody interactions to create precipitation reactions that yield results in a solution, where one type precipitates out proteins while the other precipitates intact protein complexes from solution using antibodies as precipitants.
Respectively, Herein lies the distinction between immunoprecipitation and coimmunoprecipitation: immunoprecipitation precipitates out proteins while coimmunoprecipitation precipitates intact protein complexes from solution using antibodies for both processes. thus This provides both techniques as different ways of precipitating reactions derived by antigen-antibody interaction as opposed to direct interactions.
Similarities Between Immunoprecipitation and Coimmunoprecipitation
- Both techniques can be used to detect the target antigen through a specific antibody.
- Both techniques strongly depend on antigen-antibody interactions.
- They are routinely used in clinical laboratories.
Advantages and Limitations of Immunoprecipitation and Coimmunoprecipitation
- Study of protein complexes: Coimmunoprecipitation is an invaluable method for exploring protein complexes containing multiple interacting proteins.
Detection of Protein-Protein Interactions: Coimmunoprecipitation is an invaluable way to uncover protein-protein interactions that may play essential roles in cell processes.
Validation of protein-protein interactions: Coimmunoprecipitation can be used to validate protein-protein interactions that have been discovered by other means such as yeast two-hybrid assays or mass spectrometry. - Investigation of signaling pathways: Coimmunoprecipitation can provide an efficient way to study signaling pathways by identifying proteins that interact with key signaling molecules.
Immunoprecipitation is a method that does not require special equipment or extensive training, making the method relatively simple and accessible to a range of potential researchers. There may also be limitations associated with immunoprecipitation that you need to consider. - Cross-reactivity: Immunoprecipitation can produce false positive results due to cross-reactivity between non-specific proteins and specific proteins, thus producing false positive results and leading to false positive results.
Immunoprecipitation can be challenging without commercially available antibodies, so having them on hand is critical to its success.
Immunoprecipitation has the ability to produce low yields of target proteins, especially those of low abundance, by immunoprecipitation.
Immunoprecipitation can often occur under non-physiological conditions, using harsh solvents and high concentrations of salts that can alter protein stability or activity.Coimmunoprecipitation has limitations:
- Non-specific binding: Coimmunoprecipitation can result in non-specific protein binding that can produce false-positive results, potentially giving misleadingly positive readings.
Protein stability: Coimmunoprecipitation can expose proteins to potential instability problems, especially for complexes that are difficult to isolate and purify.
Cross-linking artifacts: Coimmunoprecipitation can sometimes result in cross-linking artifacts that interfere with protein interactions or function, potentially altering protein-protein interactions or protein function. - Antibody Availability: Coimmunoprecipitation requires two specific antibodies that recognize both the target protein and its binding partner; Unfortunately these may not be commercially available or may require extensive optimization efforts before use.
Immunoprecipitation and coimmunoprecipitation are powerful techniques, yet each has unique advantages and limitations that should be considered when designing experiments or interpreting results. Researchers should take these factors into account when conducting investigations or interpreting results.
Conclusion
Immunoprecipitation (IP) and coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP) are widely employed methods in molecular biology to isolate and characterize proteins and complexes, where IP often serves to further purify them and detect modifications while co-IP provides an efficient way to study their interactions. By and complex.
Both techniques have advantages and limitations that researchers should consider when selecting the appropriate method for their specific research question. Despite some limitations, IP and Co-IP remain valuable tools in the study of protein function and interactions and have contributed significantly to our understanding of biological processes and disease mechanisms.